Read the Owners Manual first!
Difference between revisions of "I/O connectivity and levels"
| (20 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 213: | Line 213: | ||
=Setup menu= | =Setup menu= | ||
| − | Connecting devices and setting levels may require adjusting parameters in | + | Connecting devices and setting levels may require adjusting parameters in SETUP. |
=Analog output= | =Analog output= | ||
| Line 256: | Line 256: | ||
<blockquote> | <blockquote> | ||
[https://forum.fractalaudio.com/threads/thoughts-on-2-x-vp4%E2%80%99s-1-for-in-front-1-for-fx-loop-of-an-amp.208727/post-2608734] | [https://forum.fractalaudio.com/threads/thoughts-on-2-x-vp4%E2%80%99s-1-for-in-front-1-for-fx-loop-of-an-amp.208727/post-2608734] | ||
| − | Humbuster is not necessary because it's DC powered and the chassis is floating. Hum occurs due to ground loops. If equipment is AC powered the chassis must be grounded by law. This introduces ground loops when using unbalanced connections. The correct solution is for everything to be balanced but the industry seems reluctant to embrace that. | + | Humbuster is not necessary because it's DC powered and the chassis is floating. |
| + | |||
| + | Hum occurs due to ground loops. If equipment is AC powered the chassis must be grounded by law. This introduces ground loops when using unbalanced connections. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The correct solution is for everything to be balanced but the industry seems reluctant to embrace that. | ||
</blockquote> | </blockquote> | ||
</blockquote> | </blockquote> | ||
| Line 319: | Line 323: | ||
[https://forum.fractalaudio.com/threads/question-about-using-a-real-boss-hm-2-with-fractal.209004/#post-2611335] | [https://forum.fractalaudio.com/threads/question-about-using-a-real-boss-hm-2-with-fractal.209004/#post-2611335] | ||
Fractal Audio products can output up to 20dBu which is about four times what a typical drive pedal can output. | Fractal Audio products can output up to 20dBu which is about four times what a typical drive pedal can output. | ||
| + | </blockquote> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <blockquote> | ||
| + | [https://thegearforum.com/threads/how-good-are-the-fractal-ods.7257/page-2#post-297817] | ||
| + | Our products can output 20Vp-p. Likewise the inputs can handle up to 20Vp-p. | ||
</blockquote> | </blockquote> | ||
| Line 383: | Line 392: | ||
* Effects Send/Return loop for <q>guitar level</q> devices for unity gain. | * Effects Send/Return loop for <q>guitar level</q> devices for unity gain. | ||
| − | Inputs 3 and 4 support high-impedance sources, such as guitars and basses, besides other gear. They do not support the <q>[[I/O_connectivity_and_levels#Instrument_input:_Secret_Sauce|Secret Sauce]]</q> feature in the instrument input (see below) and do not support [[I/O_connectivity_and_levels#Input_Impedance|variable input impedance]]. There's a Boost/Pad parameter in | + | Inputs 3 and 4 support high-impedance sources, such as guitars and basses, besides other gear. They do not support the <q>[[I/O_connectivity_and_levels#Instrument_input:_Secret_Sauce|Secret Sauce]]</q> feature in the instrument input (see below) and do not support [[I/O_connectivity_and_levels#Input_Impedance|variable input impedance]]. There's a Boost/Pad parameter in SETUP to fine-tune their signal level for low floor noise. |
As unity gain loops, these outputs have a lower output level than the main output(s). To achieve unity gain, set the physical OUT knob to its maximum position. | As unity gain loops, these outputs have a lower output level than the main output(s). To achieve unity gain, set the physical OUT knob to its maximum position. | ||
| Line 423: | Line 432: | ||
Out 3/4 can also be used as a send to an external amp. Since they are "unity gain" you get the same gain as plugging straight into the amp. | Out 3/4 can also be used as a send to an external amp. Since they are "unity gain" you get the same gain as plugging straight into the amp. | ||
| + | </blockquote> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <blockquote> | ||
| + | [https://forum.fractalaudio.com/threads/fx-only-mode.209310/#post-2614895] | ||
| + | If you are using it in the loop of an amp you should use Input 3 and Output 3 (or Input 4 and Output 4). Input 1 is an instrument level input and you risk overdriving it. | ||
</blockquote> | </blockquote> | ||
| Line 630: | Line 644: | ||
Fractal Audio products can handle 20dBu on their inputs as well (the instrument input range is 6dB less). | Fractal Audio products can handle 20dBu on their inputs as well (the instrument input range is 6dB less). | ||
</blockquote> | </blockquote> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <blockquote> | ||
| + | [https://thegearforum.com/threads/how-good-are-the-fractal-ods.7257/page-2#post-297817] | ||
| + | Our products can output 20Vp-p. Likewise the inputs can handle up to 20Vp-p. | ||
| + | </blockquote> | ||
| + | |||
</blockquote> | </blockquote> | ||
| Line 664: | Line 684: | ||
==Input Impedance== | ==Input Impedance== | ||
| − | The inputs on the Axe-Fx II, the Axe-Fx III (front only), FM9, VP4 and FX8 feature adjustable/variable input impedance on the instrument input. | + | The inputs on the Axe-Fx II, the Axe-Fx III (front only), FM9, VP4 (L/Mono only) and FX8 feature adjustable/variable input impedance on the instrument input. |
On the FM3 and AX8, input impedance is fixed at 1M ohm. | On the FM3 and AX8, input impedance is fixed at 1M ohm. | ||
| Line 674: | Line 694: | ||
Input 2 on all devices is a LINE level port. It does not support the <q>Secret Sauce</q> and does not support variable input impedance. | Input 2 on all devices is a LINE level port. It does not support the <q>Secret Sauce</q> and does not support variable input impedance. | ||
| − | ; Axe-Fx III : Combi port (XLR + 1/4”). These ports support high-impedance sources such as guitars and basses, besides other gear. Because of this, there will be some white noise when Input 2 is connected to an output and nothing is plugged into Input 2 (this does not apply to ports 3 and 4). The signal-to-noise ratio is adjusted through Setup > Input > Input Trim. You can choose between mono or stereo input in | + | ; Axe-Fx III : Combi port (XLR + 1/4”). These ports support high-impedance sources such as guitars and basses, besides other gear. Because of this, there will be some white noise when Input 2 is connected to an output and nothing is plugged into Input 2 (this does not apply to ports 3 and 4). The signal-to-noise ratio is adjusted through Setup > Input > Input Trim. You can choose between mono or stereo input in Setup > Input 2 Mode. Use the Input 2 block on the grid to handle the input signal. |
: The Axe-Fx III and FM9 provide additional inputs. Read [[I/O_connectivity_and_levels#I.2FO_3_and_I.2FO_4_.28Axe-Fx_III.2C_FM9.29|I/O 3 and 4]] for more information. | : The Axe-Fx III and FM9 provide additional inputs. Read [[I/O_connectivity_and_levels#I.2FO_3_and_I.2FO_4_.28Axe-Fx_III.2C_FM9.29|I/O 3 and 4]] for more information. | ||
| − | ; FM9 : 1/4” port, L/R, balanced, line level. It can be used to connect an instrument. The signal-to-noise ratio and Boost/Pad can be fine-tuned in | + | ; FM9 : 1/4” port, L/R, balanced, line level. It can be used to connect an instrument. The signal-to-noise ratio and Boost/Pad can be fine-tuned in SETUP. You can choose between mono or stereo input in SETUP. Use the Input 2 block on the grid to handle the input signal. |
| − | ; FM3 : 1/4” port, L/R, balanced, line level, designed for unity gain. It can be used to connect an instrument. The signal-to-noise ratio and Boost/Pad can be fine-tuned, and you can choose between mono or stereo input in | + | ; FM3 : 1/4” port, L/R, balanced, line level, designed for unity gain. It can be used to connect an instrument. The signal-to-noise ratio and Boost/Pad can be fine-tuned, and you can choose between mono or stereo input in SETUP. Use the Input 2 block on the grid to handle the input signal. |
: For more information see Output 2 above. | : For more information see Output 2 above. | ||
| Line 803: | Line 823: | ||
; Between guitar and processor : If you want to connect an effects pedal to an amp modeler, with the processor configured for Amp and Cab modeling, connect it between the guitar and the instrument input on the processor. Remember to check the [[Input impedance]] (AX8 and FM3: n/a), and make sure the pedal's output doesn't overload the input of the unit. | ; Between guitar and processor : If you want to connect an effects pedal to an amp modeler, with the processor configured for Amp and Cab modeling, connect it between the guitar and the instrument input on the processor. Remember to check the [[Input impedance]] (AX8 and FM3: n/a), and make sure the pedal's output doesn't overload the input of the unit. | ||
| − | ; Effects loop : Alternatively, insert the effect in an effects loop. Make sure to adjust levels where needed (block(s), I/O menu, output level knob on front/top panel. You can include/exclude the effect per scene, or use the effects loop block as an audio switcher. On the Axe-Fx III, FM9, FM3 and AX8, set the Output knob to its maximum position to achieve [[I/O_connectivity_and_levels#Unity_gain|unity gain]], and use the Boost/Pad parameter in | + | ; Effects loop : Alternatively, insert the effect in an effects loop. Make sure to adjust levels where needed (block(s), I/O menu, output level knob on front/top panel. You can include/exclude the effect per scene, or use the effects loop block as an audio switcher. On the Axe-Fx III, FM9, FM3 and AX8, set the Output knob to its maximum position to achieve [[I/O_connectivity_and_levels#Unity_gain|unity gain]], and use the Boost/Pad parameter in SETUP for the used Input port to set the optimal level for low noise floor. |
Output 2 on the FM3 is designed for unity gain applications, like Outputs 3 and 4 on the Axe-Fx III. In a unity gain setup, i.e. when adding an external effects pedal to the FM3, keep the Output 2 block connected to the Input 2 block. IN 2 is specially designed to work as a bypass for the entire loop, allowing signal to flow from In 1 to Out 1 even when the outboard gear is not in use. | Output 2 on the FM3 is designed for unity gain applications, like Outputs 3 and 4 on the Axe-Fx III. In a unity gain setup, i.e. when adding an external effects pedal to the FM3, keep the Output 2 block connected to the Input 2 block. IN 2 is specially designed to work as a bypass for the entire loop, allowing signal to flow from In 1 to Out 1 even when the outboard gear is not in use. | ||
| Line 919: | Line 939: | ||
The Axe-Fx III provides a parameter to adjust ALL presets for variations in guitar output level: '''Setup : I/O : Input : Input 1 Gain'''. It trims the level of Input 1 before the start of the grid so, unlike the A/D Input Level parameters, it has an impact on blocks such as the virtual amplifier.<BR> | The Axe-Fx III provides a parameter to adjust ALL presets for variations in guitar output level: '''Setup : I/O : Input : Input 1 Gain'''. It trims the level of Input 1 before the start of the grid so, unlike the A/D Input Level parameters, it has an impact on blocks such as the virtual amplifier.<BR> | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | On the Axe-Fx III and FM9, this parameter is located in Setup > I/O. On the FM3, it's in the Global Settings. | ||
===Preset: Input block=== | ===Preset: Input block=== | ||
| Line 952: | Line 973: | ||
===Global EQ=== | ===Global EQ=== | ||
| − | Each '''Global EQ''', found in | + | Each '''Global EQ''', found in SETUP, includes a level parameter. This lets you control the overall level of the outgoing signal through that particular output port. This does not affect AES, SPDIF and USB Audio. |
===Hardware OUT knobs=== | ===Hardware OUT knobs=== | ||
| Line 1,008: | Line 1,029: | ||
<blockquote> | <blockquote> | ||
[https://forum.fractalaudio.com/threads/fm9-firmware-version-4-01.193589/post-2407777] | [https://forum.fractalaudio.com/threads/fm9-firmware-version-4-01.193589/post-2407777] | ||
| − | The instrument input max voltage is about +/- 5.9V (11.8Vpp = about 17.5 dBu). Inputs 2/3 can handle up to around 11V (about 23 dBu). If you need to set it to 5% then set it to 5%. Don't worry about it seeming low. It's just because it's a linear control. | + | The instrument input max voltage is about +/- 5.9V (11.8Vpp = about 17.5 dBu). |
| + | |||
| + | Inputs 2/3 can handle up to around 11V (about 23 dBu). | ||
| + | |||
| + | If you need to set it to 5% then set it to 5%. Don't worry about it seeming low. It's just because it's a linear control. | ||
</blockquote> | </blockquote> | ||
</blockquote> | </blockquote> | ||
| Line 1,083: | Line 1,108: | ||
<blockquote> | <blockquote> | ||
| − | [https://forum.fractalaudio.com/threads/axe-fx-iii-firmware-22-00-public-beta-beta-6.193187/post-2401863] Many things contribute: number of windings, magnet strength, distance from strings, string type and gauge, pick thickness, how hard you pick, etc. Nothing has changed in the input processing. The clip indicator trips when the input is within 0.5 dB of full-scale. If if trips you should turn down the sensitivity. | + | [https://forum.fractalaudio.com/threads/axe-fx-iii-firmware-22-00-public-beta-beta-6.193187/post-2401863] Many things contribute: number of windings, magnet strength, distance from strings, string type and gauge, pick thickness, how hard you pick, etc. |
| + | |||
| + | Nothing has changed in the input processing. The clip indicator trips when the input is within 0.5 dB of full-scale. If if trips you should turn down the sensitivity. | ||
</blockquote> | </blockquote> | ||
| Line 1,097: | Line 1,124: | ||
<blockquote> | <blockquote> | ||
[http://forum.fractalaudio.com/threads/input-gate-level-setting-can-this-be-used-as-an-analog-stage-guitar-input-pad.127000/#post-1511036] | [http://forum.fractalaudio.com/threads/input-gate-level-setting-can-this-be-used-as-an-analog-stage-guitar-input-pad.127000/#post-1511036] | ||
| − | + | The Input Trim control in the I/O menu is before the A/D. You can use that to reduce the level into the A/D. | |
| + | |||
| + | [...] | ||
| + | |||
| + | If you want 4 dB of gain reduction:<br> | ||
| + | A = 10^(-4/20) = 0.63<br> | ||
| + | So you need to reduce your input pad by 37%. The new value is 0.243 * 0.63 = 0.153 => 15.3% | ||
</blockquote> | </blockquote> | ||
| Line 1,294: | Line 1,327: | ||
* Switch off the monitors. | * Switch off the monitors. | ||
| − | * Connect the studio monitors to another output and send the Output 1 signal to that output in | + | * Connect the studio monitors to another output and send the Output 1 signal to that output in SETUP. |
* Use a line level attenuator to turn down the monitors' level without affecting the headphones level. | * Use a line level attenuator to turn down the monitors' level without affecting the headphones level. | ||
| Line 1,600: | Line 1,633: | ||
The <q>Fletcher-Munson curve</q>, or <q>Equal-loudness contour</q> is the scientific name for the fact that human ears perceive sound at low volume levels differently than at higher levels. This is VERY important when dialing in tones. | The <q>Fletcher-Munson curve</q>, or <q>Equal-loudness contour</q> is the scientific name for the fact that human ears perceive sound at low volume levels differently than at higher levels. This is VERY important when dialing in tones. | ||
| − | When tweaking tone at low volume levels, a player often turns up treble and bass. This is what the | + | When tweaking tone at low volume levels, a player often turns up treble and bass. This is what the <q>Loudness</q> switch on older home stereo systems did. |
When the volume is turned up, those high and low frequencies get harsh and boomy. That guitar sound then competes with cymbals, and will lose. Also, the guitar competes with the bass guitar, and will lose. | When the volume is turned up, those high and low frequencies get harsh and boomy. That guitar sound then competes with cymbals, and will lose. Also, the guitar competes with the bass guitar, and will lose. | ||
| Line 1,612: | Line 1,645: | ||
The "Loudness" controls in old Hi-Fi gear was nothing more than a bass/treble boost. It's a gimmick. It was supposed to compensate for the reduced sensitivity of human hearing at lower volumes. It's not accurate, never was and can never be. There are a myriad of reasons why, the most glaring is that you have no way of knowing what the SPL is (without a meter). Since equal loudness contours are dependent on SPL you can't compensate if you don't know the SPL. The Axe-Fx has no idea of the sensitivity of the amplifier and speakers connected. Therefore it can't possibly know what the SPL is and concomitantly can't know how to compensate. | The "Loudness" controls in old Hi-Fi gear was nothing more than a bass/treble boost. It's a gimmick. It was supposed to compensate for the reduced sensitivity of human hearing at lower volumes. It's not accurate, never was and can never be. There are a myriad of reasons why, the most glaring is that you have no way of knowing what the SPL is (without a meter). Since equal loudness contours are dependent on SPL you can't compensate if you don't know the SPL. The Axe-Fx has no idea of the sensitivity of the amplifier and speakers connected. Therefore it can't possibly know what the SPL is and concomitantly can't know how to compensate. | ||
</blockquote> | </blockquote> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <blockquote> | ||
| + | [https://forum.fractalaudio.com/threads/fletcher-munson-nightmare.211537/page-2#post-2646134] | ||
| + | People dial in modelers at low volumes and (usually unwittingly) compensate for F-M. Then when they turn up at a gig the lows are boomy and the highs are piercing. | ||
| + | Tube amps are voiced for gig volumes. Therefore it is logical to dial in your presets at gig volume. | ||
| + | </blockquote> | ||
</blockquote> | </blockquote> | ||
| Line 1,624: | Line 1,663: | ||
Above, we concluded that the FRFR sound has an extended frequency range, which is often undesirable for a guitar sound and can suffer from the Fletcher-Munson curve when not dialed in correctly. | Above, we concluded that the FRFR sound has an extended frequency range, which is often undesirable for a guitar sound and can suffer from the Fletcher-Munson curve when not dialed in correctly. | ||
| − | The solution to these issues is really simple: Don't dial in too much top and bottom end, and always dial in your live guitar tones at gig levels, 90dB and higher. Do NOT expect excellent | + | The solution to these issues is really simple: Don't dial in too much top and bottom end, and always dial in your live guitar tones at gig levels, 90dB and higher. Do NOT expect excellent <q>bedroom</q> or headphone tones to translate well to a rehearsal room or stage because our perception of sound changes as the volume changes. What sounds dull at low volume, may sound fantastic at high volume. And remember that the guitar is a <q>mid</q> instrument, so focus on the midrange. |
So, how do you tweak the sound for FRFR? Here are some guidelines and options: | So, how do you tweak the sound for FRFR? Here are some guidelines and options: | ||
| − | * Use the Low Cut and High Cut parameters in the Cab block to block undesirable top and bottom end. Common values are cutting lows, using | + | * Use the Low Cut and High Cut parameters in the Cab block to block undesirable top and bottom end. Common values are cutting lows, using <q>high-pass</q> between 120-150Hz and cutting highs, or <q>low-pass</q>, between 5-10kHz. This may seem to make your guitar sound bad or dull by itself, but it will improve its sound within the entire mix. |
* Put a PEQ or GEQ block at the end of the grid and block the lower and higher frequencies. | * Put a PEQ or GEQ block at the end of the grid and block the lower and higher frequencies. | ||
* Adjust Depth/Bass and Treble/Presence in the Amp block. | * Adjust Depth/Bass and Treble/Presence in the Amp block. | ||
| Line 1,678: | Line 1,717: | ||
</blockquote> | </blockquote> | ||
| − | Stick to the | + | Stick to the <q>FRFR</q> setting when simultaneously using FRFR monitoring/direct-to-FOH and a solid-state power amp and conventional guitar cab on stage. |
</blockquote> | </blockquote> | ||
| Line 1,687: | Line 1,726: | ||
==FRFR and amp/cab-in-the-room== | ==FRFR and amp/cab-in-the-room== | ||
| − | Use the parameters below to get the sound of FRFR amplification closer to the familiar | + | Use the parameters below to get the sound of FRFR amplification closer to the familiar <q>amp/cab in the room</q> sound. |
'''Cab block:''' | '''Cab block:''' | ||
| − | * use Room Level | + | * use Room Level. |
| − | * use Floor Reflections | + | * use Floor Reflections. |
| − | * use FullRes IRs to add room ambience | + | * use FullRes IRs to add room ambience. |
| − | * select a | + | * select a <q>far-field</q> IR. The stock ones have <q>JM</q> in their name. Or, select a stock cab which has been captured with a neutral mic, such as the Red Wirez ones, and set Proximity to its lowest value for simulate far-field coloring. |
| − | * create the so-called | + | * create the so-called <q>HAAS</q> effect by using two IRs in stereo, with a very short delay in the Cab block on one of them. |
| − | * use Smoothing | + | * use Smoothing. |
| − | * use Low Cut and High Cut to shave off excessive low and high frequencies and mimic the frequency range of a traditional guitar speaker | + | * use Low Cut and High Cut to shave off excessive low and high frequencies and mimic the frequency range of a traditional guitar speaker. |
| − | * add the Factory 1 - 1x4 Pig 57 IR to add body to the sound | + | * add the Factory 1 - 1x4 Pig 57 IR to add body to the sound. |
| − | * bump the middle slider of a 5-band Passive GEQ | + | * bump the middle slider of a 5-band Passive GEQ. |
'''Amp block:''' Use: | '''Amp block:''' Use: | ||
| Line 1,707: | Line 1,746: | ||
Or, use a Filter instead of a Cab block. See the following for more information: | Or, use a Filter instead of a Cab block. See the following for more information: | ||
| − | * YouTube: Fractal Friday with Cooper Carter #19 <q>[https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7xlh47VsjUw Instant Fractal | + | * YouTube: Fractal Friday with Cooper Carter #19 <q>[https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7xlh47VsjUw Instant Fractal <q>Amp in the Room</q> Tone]</q>. |
* [https://forum.fractalaudio.com/threads/amp-in-the-room.141579/#post-1677582 Cliff's walk-through] in <q>Amp in the Room?</q> in the forum. | * [https://forum.fractalaudio.com/threads/amp-in-the-room.141579/#post-1677582 Cliff's walk-through] in <q>Amp in the Room?</q> in the forum. | ||
| − | In the end, if you crave a real | + | In the end, if you crave a real <q>amp/cab in the room</q> tone from your modeler, just amplify it through a power amp and a traditional guitar speaker cabinet. |
<blockquote> | <blockquote> | ||
| Line 1,807: | Line 1,846: | ||
</blockquote> | </blockquote> | ||
| − | == | + | ==Neutral tube power amp== |
When using the amp modeler with a <q>neutral</q> tube power amp, like Fryette's Power Station, and a traditional speaker cabinet: | When using the amp modeler with a <q>neutral</q> tube power amp, like Fryette's Power Station, and a traditional speaker cabinet: | ||
| Line 1,825: | Line 1,864: | ||
For more information see <q>[https://www.thegearpage.net/board/index.php?threads/fryette-lxii-power-amp.2108247/#post-29759783 Fryette LXII power amp]</q> at TGP. | For more information see <q>[https://www.thegearpage.net/board/index.php?threads/fryette-lxii-power-amp.2108247/#post-29759783 Fryette LXII power amp]</q> at TGP. | ||
| − | == | + | ==Solid-state power amp== |
When using the amp modeler with a solid-state power amp, no tubes, like a Matrix, Seymour Duncan, or Crown, and a traditional speaker cabinet: | When using the amp modeler with a solid-state power amp, no tubes, like a Matrix, Seymour Duncan, or Crown, and a traditional speaker cabinet: | ||
| Line 1,870: | Line 1,909: | ||
[https://forum.fractalaudio.com/threads/axe-fx-iii-with-real-cab-vs-the-real-thing.191689/post-2383342] Turn Speaker Drive and Thump off to start. You may want to turn them up if you're listening at lower volumes. | [https://forum.fractalaudio.com/threads/axe-fx-iii-with-real-cab-vs-the-real-thing.191689/post-2383342] Turn Speaker Drive and Thump off to start. You may want to turn them up if you're listening at lower volumes. | ||
</blockquote> | </blockquote> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <blockquote> | ||
| + | [https://thegearforum.com/threads/those-seymour-duncan-powerstage-amps-are-utter-tripe.4567/page-17#post-280260] | ||
| + | Ignoring the effects of speaker displacement on speaker impedance the *voltage* out of a tube power amp is proportional to the speaker impedance. The speaker impedance is a function of frequency. This boosts the lows and highs. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The voltage clips at the power rails so the lows and highs clip before the midrange. Therefore when you push a tube power amp into clipping the mids get emphasized. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Negative feedback reduces the output impedance and therefore makes the voltage less dependent upon the impedance. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Most of these tube preamp things with integrated "power amp simulation" and IR loaders use a simple static EQ to model the power amp. The TMP also uses static EQ to model impedance dependency but "bakes it" into the IR (for some weird reason). | ||
| + | |||
| + | In a real speaker the impedance is dependent upon the speaker displacement. The voice coil inductance decreases as the coil leaves the gap. This makes sense because there's less magnet inside the coil and inductance is dependent upon the magnetic field. The low frequency resonance also changes with displacement via a more complex relationship. FWIW, our products model this stuff. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The moral of the story is that, yes, you can simulate a tube power amp (crudely) with a static EQ. It won't simulate the clipping but if it's a high-gain tone where the preamp is doing the distortion then it's probably good enough for that genre. | ||
| + | |||
| + | IMO "good" tube tone is a combination of preamp and power amp distortion. Relying on preamp distortion can make things sound a bit flat as preamp distortion lacks dynamics. Power amp distortion alone can be a bit flubby. If you balance the two you get a more dynamic experience with more "character". | ||
| + | </blockquote> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <blockquote> | ||
| + | [https://thegearforum.com/threads/those-seymour-duncan-powerstage-amps-are-utter-tripe.4567/page-18#post-280286] | ||
| + | A speaker responds to the voltage on its terminals. If you model everything accurately and then simply amplify that signal and send it to a speaker the results will be the same. The hard parts are modeling it accurately and amplifying it correctly. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Modeling it accurately means modeling the speaker impedance which is often not known and accurately modeling the I-V relationship of the power tubes. The latter is extremely difficult and requires a lot of processing power. Inexpensive products use waveshaping and EQ approaches. We use nonlinear ODEs and iterative solvers. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Amplifying it correctly means an amplifier with significant power reserves. Most of these small, cheap Class-D amps simply don't have the power reserves to replicate a cranked 100W tube amp. The transient response is lost because the amplifier runs out of energy. They aren't designed for these sorts of applications. They're meant for low-cost consumer applications. | ||
| + | |||
| + | High-end solid-state amps, whether Class-AB, Class-D, Class-G, etc. (i.e. Crown, QSC, etc.) have the requisite energy reserves and I bet anyone would be hard-pressed to tell the difference in an A/B test (assuming the speaker impedance were set correctly). | ||
| + | |||
| + | I've done tests comparing various 100W amps using a Crown K2 and, a Matrix (something, forget the actual model but it was 1000W+) . The differences were negligible IMO. In fact, I could tweak the speaker impedance curve and end up with something that actually sounded better. | ||
| + | |||
| + | It really depends on your application. At loud stage volumes an inexpensive Class-D power amp isn't the right tool for the job. In a small club application then it's probably fine. Don't confuse misapplication with some nebulous physical shortcoming of the various technologies. | ||
| + | </blockquote> | ||
| + | |||
</blockquote> | </blockquote> | ||
| Line 1,990: | Line 2,062: | ||
In all of the above cases, turn the front panel output knob fully open for unity gain, adjust Boost/Pad in the I/O menu for optimal SNR, and adjust levels where needed. | In all of the above cases, turn the front panel output knob fully open for unity gain, adjust Boost/Pad in the I/O menu for optimal SNR, and adjust levels where needed. | ||
| − | '''VP4''' – The VP4 has a dedicated 4CM configuration mode in | + | '''VP4''' – The VP4 has a dedicated 4CM configuration mode in SETUP and must be used with dedicated 4CM presets. Read the section in its [[Owners_Manuals|Owners manual]] and its [[Owners_Manuals|4CM guide]], and read this: [[VP4#4CM|4CM]]. |
'''Axe-Fx II''' – Adjust Boost/Pad and Input Level in the I/O menu to optimize the signal. Also, turn the Output Level knob fully open for unity gain. You can't combine 4CM with cab modeling. | '''Axe-Fx II''' – Adjust Boost/Pad and Input Level in the I/O menu to optimize the signal. Also, turn the Output Level knob fully open for unity gain. You can't combine 4CM with cab modeling. | ||
| Line 2,087: | Line 2,159: | ||
</blockquote> | </blockquote> | ||
<blockquote> | <blockquote> | ||
| − | [https://forum.fractalaudio.com/threads/new-noise-buzz.184633/post-2277824] If you are going into the front of an amp and using the FM3 for effects only then use Output 2 and increase the Boost/Pad in | + | [https://forum.fractalaudio.com/threads/new-noise-buzz.184633/post-2277824] If you are going into the front of an amp and using the FM3 for effects only then use Output 2 and increase the Boost/Pad in SETUP. This will optimize the SNR. |
</blockquote> | </blockquote> | ||
</blockquote> | </blockquote> | ||
Latest revision as of 21:49, 8 June 2025
Contents
- 1 Audio jargon
- 2 Setup menu
- 3 Analog output
- 4 Input
- 4.1 Instrument input
- 4.2 Instrument input: Secret Sauce
- 4.3 Input Impedance
- 4.4 Inputs 2, 3 and 4
- 4.5 Switching between guitars
- 4.6 Multiple simultaneous instruments
- 4.7 Acoustic instruments
- 4.8 Bass guitar
- 4.9 MIDI Guitar
- 4.10 External effects
- 4.11 Wireless receiver
- 4.12 Microphone
- 4.13 Bluetooth not supported
- 5 Levels
- 5.1 About levels in the Axe-Fx III, FM3 and FM9
- 5.1.1 Introduction
- 5.1.2 Hardware A/D Sensitivity Levels
- 5.1.3 Digital Audio Input
- 5.1.4 Input 1 Gain
- 5.1.5 Preset: Input block
- 5.1.6 Preset: Amp block
- 5.1.7 Preset: More about blocks
- 5.1.8 Preset: Output block
- 5.1.9 Preset: Level Meters
- 5.1.10 Global EQ
- 5.1.11 Hardware OUT knobs
- 5.1.12 Nominal Output Level
- 5.1.13 Downstream Gear
- 5.1.14 I/O Loops
- 5.1.15 A final word...
- 5.2 Main input level
- 5.3 Main output level
- 5.4 Preset levels
- 5.1 About levels in the Axe-Fx III, FM3 and FM9
- 6 Headphones, In-Ear Monitoring (IEM)
- 7 Full Range Flat Response amplification (FRFR)
- 7.1 Why use FRFR monitoring
- 7.2 Which systems are FRFR
- 7.3 Close-miking
- 7.4 Fletcher-Munson
- 7.5 Fighting extended frequencies and Fletcher-Munson
- 7.6 Optimize the Amp block's Output Mode
- 7.7 Recommended Amp and Cab settings
- 7.8 FRFR and amp/cab-in-the-room
- 7.9 Do not put a microphone in front of a FRFR speaker
- 7.10 Tweeter squeal from FRFR speakers
- 8 Power amp and guitar speaker
- 8.1 Why use a power amp and guitar speaker
- 8.2 Using a tube power amp for guitar or head or combo
- 8.3 Neutral tube power amp
- 8.4 Solid-state power amp
- 8.5 Finding the resonant frequency with a solid-state amplifier
- 8.6 Gain-staging a power amp
- 8.7 About speaker wire/speaker cable
- 8.8 Recommended Amp and Cab settings
- 8.9 Combine FRFR with a traditional backline rig
- 8.10 4CM (Four Cable Method)
- 9 Effects only (Pre and Post)
- 10 Digital I/O and audio
- 11 IR loader
- 12 Surround or quadraphonic sound
- 13 FX8
- 14 Videos
Audio jargon
Line level, instrument level, microphone level
- Microphone level
- The lowest output level (often -60 dbV), as used in microphones and on microphone inputs on mixers.
- Instrument level
- The output level of guitars, basses etc., and effects pedals.
- Line level
- The loudest output level. Line level can be:
- Consumer audio: -10 dBv (0.316 volts).
- Professional audio: +4 dBu (1.23 volts). Commonly used in 19" processors, line inputs on mixers and monitors. With analog circuitry, this has the most headroom before clipping.
The outputs on Fractal Audio gear operate at line level. Some devices are adjustable between +4 dBu and -10 dBv. The Axe-Fx III, FM9 and FM3 default to -10 dBv, to prevent overloading mixer inputs.
FRACTAL AUDIO QUOTES
[1] The difference between -10 and +4 is roughly 12 dB.
[2] -10 dBV is compatible with instrument levels.
See these pages for more information:
- Wikipedia: Line Level and
Nominal Level
- Sweetwater: What’s the difference between Mic, Instrument, Line, and Speaker level signals?
- Record, Mix & Master: Mic, Line and Instrument Level – What’s the Difference?
Balanced and unbalanced signal
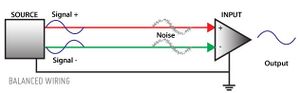
- Unbalanced audio signal
- A signal carried over a two-conductor cable. The most common cable is a 1/4” guitar cable, where the ground wire wraps around the positive wire. Unbalanced cables are generally good for running signal up to several meters (< 10).
- Balanced audio signal
- A signal carried over a three-conductor cable which connects a balanced input and balanced output. The two signal wires carry identical copies of the signal, with one of the wires 180 degrees out of phase with the other, creating a differential. At the receiving side the two signals are brought back into phase with one another, resulting in canceling of induced noise and a louder signal. These cables usually use XLR or Tip-Ring-Sleeve (TRS) connector end-types. The ground wire wraps around the signal wires and acts as a shield. A balanced connection supports the use of a ground lift switch and noise-free long cable distances.
DI (Direct Inject
) boxes transfer a high-impedance unbalanced signal, like a direct signal from a guitar or keyboard, into a balanced low-impedance signal, to avoid loss of signal and tone through long cables.
Note that a Humbuster signal is different from an XLR balanced signal.
Read Wikipedia's Balanced line
article for more information.
FRACTAL AUDIO QUOTES
[3] XLR is only necessary for long cable runs where there is the danger of picking up interference on the cable. Anything less than, say, 10 meters and unbalanced is fine.
PREVIOUS GENERATIONS
Axe-FX II:
[4] The unbalanced and XLR outputs are the same level in the Axe-Fx II. In the original Axe-Fx the XLR outputs were 6 dB hotter. This is not the case with the II.
FX8:
[5] For most uses an unbalanced TS cable is fine. The inputs are balanced so that you can get even more hum rejection by using a TS-to-TRS cable from the amp's send.
Unity gain
- What is unity gain?
- Unity gain means that the input level is equal to the output level.
- When does unity gain matter?
- It is not important when connecting the device to an amplifier or mixing console. It is important in setups where the device is being used as an effects-only processor (e.g. as a pedalboard or in an amp's effects loop) or when using the Four-Cable-Method (4CM) to connect to a guitar amplifier.
- How do I set up for unity gain?
- To set up an output for unity gain, set the corresponding Output knob to its maximum position. Note: this does not apply to all devices, check the manuals. It does apply to outputs 3 and 4 on the Axe-Fx III, output 3 on the FM9, and output 2 on the FM3.
- To test unity gain
- Use a routing of only shunts, and you should get exactly the same signal at the output which you put in. "Using real amp + load box with Axe FX (problem?)" is another example.
FRACTAL AUDIO QUOTES
[6] Unity gain mode is a special mode designed for use with the 4CM. When you turn the output levels all the way up whatever you put in you get out (assuming all unity-gain blocks in the chain). If you have an amp block in the chain then you have tons of gain and therefore no longer have unity gain.
[7] With the Axe-Fx volume all the way up you would be pushing +20dBu into the amp which could clip the inputs to the amp. Unity gain mode is only desirable for 4-cable-method.
PREVIOUS GENERATIONS
FX8 and unity gain (from the FX8 Owner's Manual):
Q: Why do I care that the FX8 is designed for unity gain?
A: The FX8 makes it EASY to achieve unity gain. This can be important because amplifier tone, distortion amount, dynamics and noise are level dependent. With unity gain:
- The level of the signal from your guitar output can reach your amp input without being altered. Therefore, your guitar-amp interaction sounds and feels the same, offering a transparent playing experience while using the FX8.
- The level of your FX SEND can reach your FX return without being altered. The entire system can therefore perform optimally, without unpredictable changes to level, dynamics or noise when you engage True Bypass or bypass all post-effects.
Q: How do I set up the FX8 for unity gain?
A: You don’t need to! Just set up according the basic instructions in Section 3. A default empty preset should sound have the same level as True Bypass Mode.Q: What might I do to inadvertently upset unity gain?
A: Many SETUP and EFFECT parameters change the gain level. Some of these are intended to change gain levels (how else is a boost supposed to work, after all?) Here is a short list of things to consider:
- The LEVEL parameter of every effect increases or decreases the overall level.
- Changing MIX on certain effects changes both dry and wet levels. This is to prevent signals from “stacking up” and causing clipping. You can compensate with your ears by turning effects on and off and comparing the level with True Bypass engaged.
- If you’re going to change a block’s BYPASS MODE from the default setting of THRU, it is best to check its levels when you engage/disengage the effect BEFORE you switch to something like MUTE FX IN.
- The level parameters on the OUTPUT page of the main mode menu increase or decrease overall levels. Incorrect settings on the I/O: AUDIO page can result in gain changes.
- The NOISE GATE has a level control.
- If your rig is MONO, every BALANCE or PAN control can affect levels.
- The Global Graphic EQs affect overall level.
- The I/O LEVEL page settings DO NOT affect unity gain. Each setting is compensated internally.
Q: Any last words of advice?
A: Use the TRUE BYPASS switch as a way to make sure your presets and scenes are on track. In general, it is better to be in control of your levels than to be fixated on the “concept” of unity gain. Do what sounds best to you and learn as much as you can about your gear.
Decibels
A decibel can mean lots of things, there are dB, dBu, dBm, dBv, dBV....
In audio +3dB means that the power is doubled, and -3dB means it is halved. However, doubled
doesn't mean two times as much, but ten times as much, because decibels operate on a logarithmic scale.
Wikipedia has more information in their Decibel
page.
FRACTAL AUDIO QUOTES
Cliff's Tech Note about the decibel (dB):
[8] The formula for the decibel is dB = 10 * log_10(P1 / P2) where P1 and P2 are power measurements. The reason it is called a decibel is because it is 10 bels. One bel would be log_10(P1/P2).
The important thing to understand is that the decibel is a RATIO of powers. A dB is meaningless without a reference power. So if someone says "that signal is 86 dB" that is a meaningless number as it has no reference.
Decibels are convenient because they convert logarithmic perception to a linear scale. Human hearing, for example, is logarithmic. Many other natural phenomena are logarithmic which means that the phenomena exists in the "multiplication domain" as opposed to the "addition domain". For example, human vision is logarithmic. We perceive light such that the light must double for it to appear twice as bright. If we were to plot that we would have an exponential curve of light intensity vs. perceived brightness. If we take the logarithm of the intensity instead we get a straight line. This is why cameras use f-stops which are a base-2 logarithm.
So, back to reference levels. There are many reference levels used in dB: dBm, dBu, dBV, dB re. kPa, etc. dBm refers to the power referenced to one milliwatt. If the measured power is, say, 100 mW then that would be 10 * log10(100/1) = 10 * log10(100) = 20 dBm. dBV is a voltage ratio and not really a true dB but, regardless, is still commonly used. The formula for dBV is 20 * log10(V1/V2) since we need to square the voltage to get the power.
In audio a common unit is dBu. dBu is the power relative to the voltage into a 600 ohm resistor that is dissipating 1 mW. This is roughly 0.77 volts. Back in the early days of telecom 600 ohms was the standard termination impedance, hence the dBu. Most pro audio gear runs at +4 dBu. What does that mean? 0 dBu is 0.77 volts so +4 dBu would be 4 dB greater, or about 1.22 volts. To go from dB to volts the formula is 10^(dB/20).
Consumer audio gear usually runs at -10dBV, or roughly 0.32 volts.
When recording your goal is to get your signal level near the nominal signal level of the equipment being used. This ensures the best S/N ratio. Many recording consoles use VU meters which are calibrated such that "0 dB" is +4 dBu. The goal is to get your signal level around 0 dB.
Well-designed gear has some amount of "headroom". Headroom is the difference between the maximum signal level and the nominal signal level. For example, the Axe-Fx II has a maximum signal level of +18 dBu. If operating at +4 dBu nominal this gives 14 dB of headroom which means that any signal peaks can be over four times higher.
In digital gear we encounter the dBFS, which is dB relative to full-scale. Full-scale is a term that indicates the maximum signal level into or out of an A/D or D/A converter, respectively. With digital converters the best performance is achieved by operating the converter such that the nominal signal level is close to full-scale. The exact voltage is unknown and irrelevant. Most digital gear will have indicators that measure the levels relative to the converter's full-scale value. For example, the input meters on the Axe-Fx indicate the input signal relative to the A/D converter's full-scale value. The "tickle the red" advice aims to operate the A/D converter near its full-scale value as the red LEDs light at 6 dB below full-scale, or -6 dBFS.
[9] Decibels are decibels. There is no such thing as "root-power decibels".
By definition a decibel (dB) is a ratio of two powers. The formula is 10 * log10(P1/P2) where P1 and P2 are the power of two signals, respectively.
In electronics, however, we usually manipulate and measure voltage levels. It's convenient to represent the ratio of two voltage levels in dB. To do this you would need to square the voltage to get the power (since P = V^2 / R). We also assume R = 1 for convenience. With a little math you get dB = 20 * log10(V1/V2).
Therefore if we reduce the voltage level of a signal by a factor of 0.1 then the signal is now -20 dB relative to before.
dB is simply an easy-to-read logarithmic-to-linear mapping. Music, human perception, and many other things in nature typically have a logarithmic response. The decay of, for example, a cymbal is logarithmic. If you plot this on a linear axis it's hard to display because of the dynamic range. But if you use a logarithmic axis you "compress" the data into something that's easier to view. Decibels are just a widely accepted mapping. You could use any base for the log; log2, ln, etc but since we have 10 fingers log10 is nice.
The point is that X dB is X dB. If you reduce a signal by 20 dB you've reduced its voltage to 10% of what it was previously. You also reduced its power to 1% of what it was previously. These are the same things: 20 * log10(0.1) = 10 * log10(0.01).
Mono and stereo
See Mono and stereo
for more information.
Latency
See Latency
for more information.
Ground lift (audio)
The ground lift switch on Fractal Audio gear is an audio
ground lift, which reduces 60 Hz cycle hum, it does not cure EMI noise picked up by your guitar or bass.
FRACTAL AUDIO QUOTES
[10] A "power" ground lift is something completely different. Do NOT lift the ground of a power connection, it's extremely dangerous.
[11] Many products do not properly terminate the ground on their XLR inputs. Ideally the cable shield should be grounded at one end only (preferably at the output) and connected to signal ground via a capacitor at the other end. However many, and in fact most, products simply ground the cable shield which can cause a ground loop. The ground lift switch breaks the ground loop.
A ground loop occurs when current flows in the shield. This happens if two devices have different ground potentials which can occur when plugged into different outlets with different ground potentials or if if the ground path creates a large loop area. In a perfect world ground potentials would be the same everywhere but this is rarely the case. A large loop area creates an inductor and any magnetic field intersecting that loop normal to the plane of the loop will induce current in the loop. Using short cables and keeping power cords bundled together helps reduce the loop area.
Lifting the ground on a cable shield does NOT present a safety hazard as this is not the means of grounding the chassis. The chassis is grounded via the power cord. It is important for the chassis to be grounded in the case of a fault condition. The insulation between the AC power and the chassis can fail. If the chassis is grounded this will cause the breaker to trip. If the chassis is not grounded the chassis can then become energized exposing the user to lethal voltages.
Lifting the ground on a computer is extremely bad practice. PC power supplies are notoriously inexpensive (i.e. cheap Chinese junk) and AC faults are not unusual. Lifting the ground can expose the user to deadly voltages. Furthermore lifting the ground on your PC will typically make any interference problems worse as the chassis is then floating. For proper shielding the chassis needs to be grounded and grounded well (and not have any stupid windows).
NEVER, EVER use a cheater plug as a ground lift. If you need to break a ground loop the first place to do it is at the audio cables. If it is an unbalanced cable you can do this simply by disconnecting the shield ground at one end, preferably the receiving end. If it's a balanced cable you can use the ground lift switch if so equipped. If there is no ground lift switch you can disconnect the shield ground inside the connector. You can buy XLR cables with the ground only connected at one end. Fractal Audio products use our proprietary "Humbuster" outputs which cancel shield ground noise.
As an absolute last resort you can use a ground isolator like an Ebtech Hum-X. This lifts the chassis ground by using a pair of diodes in anti-parallel. In the event of a AC fault the diodes will conduct tripping the breaker (hopefully before the diodes fail). Under normal operating conditions the chassis will be floating which will break the ground loop.
Oh, and I should add that the intended use of a cheater plug is to adapt a two-prong outlet to a three-prong cord by utilizing the faceplate mounting screw as a safety ground. Prior to the introduction of Romex, plastic junction boxes and three-prong outlets residential wiring used metallic conduit and metallic outlet boxes. Therefore the outlet box was grounded. A cheater plug then allows adapting a three-prong power cord to the old style outlet boxes by connecting the ground wire to the outlet box via the faceplate mounting screw. A cheater plug is NOT intended to be used as a ground lift.
[12] They are safe when used properly. If your 2 prong outlets have metal boxes and conduit and the conduit is earthed then you remove the screw from the wall plate, plug the adapter in and replace the screw. Ground is provided via the screw. They're unsafe when people use them to lift the ground. The chassis of the connected device is then not earthed. If a fault occurs whereby the line voltage is shunted to the chassis the chassis is then live which presents a shock hazard.
See Help! New PC, new noise!
in the forum for more information about computer noise and ground loops.
Connecting devices and setting levels may require adjusting parameters in SETUP.
Analog output
Axe-Fx III
- OUTPUT 1 – XLR, L/R, balanced, ground lift switch, 600 Ohm, +20dBu line level
- OUTPUT 1 – 1/4" phone jack, L/R, HumBuster, ground lift switch, 600 Ohm, +20dBu line level
- OUTPUT 2 – XLR, L/R, balanced, ground lift switch, 600 Ohm, +20dBu line level
- OUTPUT 3 – 1/4" phone jack, L/R, HumBuster, 600 Ohm, +20dBu line level
- OUTPUT 4 – 1/4" phone jack, L/R, HumBuster, 600 Ohm, +20dBu line level
FM9
- OUTPUT 1 – XLR, L/R, balanced, ground lift switch, 600 Ohm, max. +20dBu line level, selectable between -10 dBV / +4 dBu
- OUTPUT 1 – 1/4" phone jack, L/R, HumBuster, ground lift switch, 600 Ohm, max. +20dBu line level
- OUTPUT 2 – XLR, L/R, balanced, ground lift switch, 600 Ohm, max. +20dBu line level, selectable between -10 dBV / +4 dBu
- OUTPUT 3 – 1/4" phone jack, L/R, HumBuster, 600 Ohm, max. +20dBu line level
FM3
- OUT 1 / MAIN – XLR, L/R, balanced, ground lift switch, line level
- OUT 2 / FX SEND - 1/4” phone jack, L/R, Humbuster, line level, designed for unity gain
VP4
- OUT — 1/4" phone jack L/R, 600 Ohm, 16dBu, unbalanced, no Humbuster
FRACTAL AUDIO QUOTES
[13] All of the outputs on the VP4 are unbalanced.
[14] Humbuster is not necessary because it's DC powered and the chassis is floating.
Hum occurs due to ground loops. If equipment is AC powered the chassis must be grounded by law. This introduces ground loops when using unbalanced connections.
The correct solution is for everything to be balanced but the industry seems reluctant to embrace that.
Output 1
Output 1, the main Out, on the amp modelers is usually used for the direct signal, including cabinet modeling. Most presets, including the factory presets, are set up this way.
The Output 1 block provides the output gain of the Axe-Fx III (20dBu), FM3 and FM9 devices, even with the Level parameter at 0. This can be monitored by connecting the Input 1 block directly to the Output 1 block and looking at the meter in the Output block.
There’s no difference between the outputs on the Axe-Fx III, FM3 or FM9 apart from the output level.
Except for the FM3, which is XLR only, the amp modelers provide both XLR and 1/4” Output 1 ports, which can be used simultaneously. They're buffered. XLR ports are protected against phantom power from the console.
FRACTAL AUDIO QUOTES
[15] The outputs are buffered.
[16] All Fractal Audio products have phantom power blocking on the XLR outputs.
[17] The XLR outputs on the Axe-Fx III are phantom power tolerant. It is recommended, however, to turn phantom power off before connecting or disconnecting cables as long cables can cause an inductive kick. The Axe-Fx III has catch diodes to protect against the inductive kick but it's still safer to turn the power off.
[18] The outputs are electrically identical. The idea is that one is FOH and the other is your personal monitoring. You can change the volume of your personal monitoring without affecting the FOH.
[19] Output gain accuracy is +/- 0.2 dB.
[20] FX III is 6 dB higher than FM3 on Output 1.
[21] The outputs have mute circuits that activate at power up and power down. The FM3 and FM9 also have this circuitry.
[22] The Axe-Fx III is NOT intended to be connected to microphone preamps. It is a LINE LEVEL device and is intended to be connected to a high impedance line-level input. Line level inputs typically have input impedances of 10K or more (usually much more - 100K - 1M).
Theoretically the "optimum" input impedance matches the output impedance of the source. This provides maximum POWER transfer and hence best SNR. For line-level devices, however, SNR is not a concern so the input impedance is typically designed to be quite high (10K+).
[23] Fractal Audio products can output up to 20dBu which is about four times what a typical drive pedal can output.
[24] Our products can output 20Vp-p. Likewise the inputs can handle up to 20Vp-p.
PREVIOUS GENERATIONS
Axe-Fx II
[25] Both outputs should work simultaneously. They are actually buffered so even if you shorted one it shouldn't affect the other.
Output 2, I/O 2
Output 2 on the amp modelers can be used:
- as an auxiliary mono/stereo output.
- with Input 2 as a mono/stereo effects loop (Output 2 = Effects Send, Input 2 = Effects Return).
When set up as an auxiliary output, you can set the level of Output 1 (usually FOH) separately from that of Output 2 (usually monitors).
- Axe-Fx II and AX8: Output 2 is a set of 1/4" ports. To enable I/O 2 on the layout grid, use the FX Loop block.
- Axe-Fx III and FM9: Output 2 is a set of XLR ports. If you need to feed an output signal to an external power amp, avoid Output 2 if possible, because it doesn't allow the use of 1/4" Humbuster cables.
FRACTAL AUDIO QUOTES
Axe-Fx III, FM9, FM3:
[26] The outputs have mute circuits that activate at power up and power down. The FM3 and FM9 also have this circuitry.
[27] All Fractal Audio products have phantom power blocking on the XLR outputs.
FM3:
The FM3's Output 2 is a set of 1/4" ports. Unlike the Axe-Fx III and FM9, Output 2 on the FM3 is designed for unity gain applications, like Outputs 3 and 4 on the Axe-Fx III (see below). Crank the Level knob for unity gain. In a unity gain setup, i.e. when adding an external effects pedal to the FM3, keep the Output 2 block connected to the Input 2 block. IN 2 is specially designed to work as a bypass for the entire loop, allowing signal to flow from In 1 to Out 1 even when the outboard gear is not in use.
[28] Output 2 is primarily designed as a unity-gain output for use as an effects loop. To get more level to drive your monitors use an Output 2 block and turn up the Level in the block.
I/O 3 and I/O 4 (Axe-Fx III, FM9)
- Axe-Fx III
- Two additional 1/4” I/O pairs: I/O 3 and I/O 4.
- FM9
- One additional 1/4” I/O pair: I/O 3.
- FM3
- I/O 2 on the FM3 operates the same as I/O 3 and 4 on the Axe-Fx III.
These stereo pairs are designed primarily for inserting outboard gear such as rack and pedal effects, for using the Four Cable Method (4CM
), for guitar level
input devices, and to connect to amplifiers and other purposes. In other words, use these ports as an additional:
guitar level
instrument input.- output for unity gain.
- Effects Send/Return loop for
guitar level
devices for unity gain.
Inputs 3 and 4 support high-impedance sources, such as guitars and basses, besides other gear. They do not support the Secret Sauce
feature in the instrument input (see below) and do not support variable input impedance. There's a Boost/Pad parameter in SETUP to fine-tune their signal level for low floor noise.
As unity gain loops, these outputs have a lower output level than the main output(s). To achieve unity gain, set the physical OUT knob to its maximum position.
Using I/O 3 or 4 as an effects loop introduces a small signal latency. The same applies to Output 2 on the FM3.
For more information read FM3 Internal/Passthrough Latency Measurements - Surprising Results?
in the forum.
FRACTAL AUDIO QUOTES
[29] All Fractal Audio products have phantom power blocking on the XLR outputs.
[30] […] output 1 and 2 have a higher output level.
[31] Outputs 3 and 4 are primarily intended for unity gain applications, i.e. fx loops. You can use them as general-purpose outputs as well. When doing this you may need to increase the Output Level of the associated Output block.
[32] Outputs 3 and 4 are "unity gain" and have a different gain constant via the internal number representation than 1 and 2. They are designed for effects loop use, DI sends, etc. If you put 1V into Input 1 and route that to Output 3 and turn its Level knob to maximum you'll get 1V out.
[33] […] Out 3/4 are designed for "unity gain" with respect to an input. If you put 1V into an input, connect that input to Out3 and turn the Level knob on the front panel all the way up you'll get 1V out. This makes it easy to use them as loops for pedals, etc.
The effective difference is about 18 dB if Out1/2 are set to +4 dBu, 6 dB if set to -10 dBV.
Out 3/4 can also be used as a send to an external amp. Since they are "unity gain" you get the same gain as plugging straight into the amp.
[34] If you are using it in the loop of an amp you should use Input 3 and Output 3 (or Input 4 and Output 4). Input 1 is an instrument level input and you risk overdriving it.
[35] If you want more signal at those outputs you need to put those Output blocks in the preset and increase the Level in the block. Outputs 3 & 4 are primarily intended to be unity gain outputs for fx loop use.
[36] When routing a signal from Input 1 to Output 3 or 4 it's entirely possible for the meters to enter the red zone. This is not an issue.
[37] Outputs 3 and 4 are intended to drive "guitar level" devices.
[38] Outputs 3 and 4 are "unity gain" and have a different gain constant via the internal number representation than 1 and 2. They are designed for effects loop use, DI sends, etc. If you put 1V into Input 1 and route that to Output 3 and turn its Level knob to maximum you'll get 1V out.
[39] […] If you turn the Output 3 Level knob on the front panel all the way up you'll get a buffered copy of your guitar's signal. Instrument level is neither -10 or +4. It's instrument level. However for your purposes -10 will probably work best.
-10 dBV is a nominal peak level of around 0.5V. Equipment is usually designed to have headroom of 12 to 18 dB. That infers the max peak level would be 2 to 4 V which is sufficient for a typical guitar. Some guitars have really hot pickups which may require +4.
[40] Channels 3 and 4 are not phantom power tolerant as they are 1/4" jacks. However if you plugged them into your mixer using 1/4" cables then you're fine. A mixer only applies phantom power to XLR inputs.
[41] The outputs have mute circuits that activate at power up and power down. The FM3 and FM9 also have this circuitry.
[42] If you are using both loops along with the analog in and out then it's around 3ms.
OTHER QUOTES
Forum member Patzag:
[43] The exact boost needed to match a MAXED OUT Out 1at +4dBu is 19.5 dB. The exact boost needed to match a MAXED out Out 1 at -10dBV is 7.1 dB.
How to configure I/O 3 and 4
- Select mono or stereo in Setup.
- Adjust Boost/Pad in Setup, if necessary.
- Set the optimal signal-to-noise level in Setup > Input Trim.
- Decide whether to use unity gain. To set these loops to unity gain, which is their primary purpose, turn the corresponding hardware knobs to their maximum position. Unity gain means that the output level from the unit is the same as the unit's input level. This makes it easy to use these ports for pedals. And as a send to an external amp, because "unity gain" means that you get the same gain as plugging straight into the amp.
- Use the corresponding Input and Output blocks on the grid to route the signal. Note that you do NOT need to connect the Output block to the Input block on the grid.
How to create an effects loop
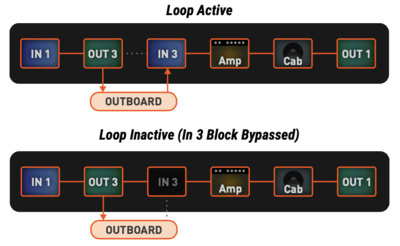
To establish an effects loop and integrate an external device like a pedal, an entire pedalboard or a rack, use I/O pair 3 or 4 on the Axe-Fx III, or I/O 2 on the FM3 or I/O 3 on the FM9. The Output block is the Effects Send, the Input block is the Effects Return. Connect the Output block to the grid to feed the external device a signal. Keep the Output block settings at default. Turn off the noise gate in the Input block. Connect the Input block to the grid to let the signal from the external device enter the grid. The Output and Input blocks do NOT have to be connected to each other. Now turn up the Output knob on the front panel to its maximum position, this makes sure that the loop is operating at unity gain.
- If the Output block is:
- not connected to the Input block, and the Input block is bypassed, the signal from the effects loop is muted.
- connected to the Input block, and the Input block is bypassed, the signal is passed without going through the effects loop.
- connected to the Input block and the Input block is engaged, the signal from the effects loop is passed.
From the Blocks Guide:
The “FX Loop” block found on previous products no longer exists. Instead, individual Input and Output blocks must be placed separately on the grid. In the example below, signal flows (in red) from the Output block to outboard gear and back through the Input block. The Input block serves as a “master bypass” control for the send/return loop. The Output block on the grid is connected with a cable to the Input block as shown below, but the Input block ignores grid input signals when it is engaged (below, left image) and ignores external input signals when it is bypassed (below, right image).
When using the Input block as the on/off switch for the loop no sound will enter the grid if the loop is off, however this will also cut off tails from effects such as delay when turning off the loop.
How to connect to a power amp
If you need to feed an output signal to an external power amp and you have to choose between Output 2, 3 or 4, use 3 or 4. These outputs allow the use of 1/4” Humbuster cables.
How to insert another Fractal Audio processor in an Axe-Fx III effects loop
- Connect Output 3 on the Axe-Fx III to the input on the other device.
- Connect the output of the other device to Input 3 on the Axe-Fx III.
- Turn up Output 3 on the front panel of the Axe-Fx III.
- In the Axe-Fx III preset, connect IN1 to OUT3 and IN3 to OUT1.
- When IN3 is bypassed, it just passes the III signal.
- When IN3 is engaged, you'll hear the other device.
FRACTAL AUDIO QUOTES
[44] I use loops in front of the amps all the time. The key is to get the gain staging right. Increase the commensurate boost/pad as high as possible without clipping the output. Make sure the associated output level knob on the front is turned all the way. Adjust the Input Trim for the associated input as high as possible without clipping the input. That said, you won't lose the "secret sauce" by putting a pedal in front.
How to test an output port
FRACTAL AUDIO QUOTES
Axe-Fx III
[45] It's even easier as you can use the RTA block.
PREVIOUS GENERATIONS
[46] One way you can test the I/O is to use the synth block. Set the oscillator to pink noise and route it to the various outputs. Be sure to set the filter to 20 kHz (default is 10). Check the spectrum with your analyzer plug-in. It should be flat. You can then route the output of the synth to Output 2 and then jump Output 2 to the Inputs and route the inputs to Output 1 to make sure the inputs are working properly. Route it directly to the Output to test Output 1. Route it only to the FX Loop block to test Output 2. Then run a short cable from Output 2 to the front panel Input to test the input. Run a line of shunts from the input to the output.
Input
Instrument input
- Axe-Fx III – INSTRUMENT (front and rear, auto-switching)
- FM9 – INSTRUMENT (rear)
- FM3 – In 1/INSTRUMENT (rear)
- VP4 – Input L/R (rear)
- Axe-Fx II – INSTR (front)
- AX8 – IN 1 (INSTRUMENT)
- FX8 – IN 1 (PRE)
The Instrument input uses a proprietary circuit and a dedicated A/D converter to reduce noise. It's conditioned for guitar through hardware and software, AKA Secret Sauce
. For best results, use the instrument input for guitar, whether wired or wireless, electric or acoustic, except when running a line level signal.
Make sure that you do NOT use a balanced
instrument cable between the instrument and input. You can recognize these kind of cables by their stereo
TRS jacks.
The Axe-Fx III has two instrument inputs: front and rear. The rear is meant to be used with racks, wireless units and such. Using the front input, for example with a cable, ALWAYS overrides the rear input, and this does not require a configuration change in Setup. Note however, the rear input doesn't provide auto-switching input impedance.
FRACTAL AUDIO QUOTES
If you think the input is faulty:
[47] Here's a way to test the input:
- Go to a blank preset.
- Create a chain that connects Input 1 to the RTA block. On a separate row create a chain where the Synth block feeds Output 3.
- Set the Synth Type = Sine, Tracking = Off, Frequency = 1000 Hz.
- Connect an instrument cable from Output 3 (left or right) to the Instrument Input.
- Set the Input 1 / Instrument A/D Input Level (Home->Setup->I/O) to 50%.
- Turn the Out 3 Level knob all the way up.
The Input 1 yellow LED should be lit. Red should not be lit. Go to the RTA block Config tab. Set Bands to 128, Window to Blackman. Go to the RTA tab. There should be a narrow spike at 1 kHz (three bands). There should be no other bands showing power except maybe a little noise at the highest bands. The spike at 1 kHz should be about 2 1/4 divisions below full-scale.
Axe-FX III:
[48] The front and rear inputs are identical on the III.
[49] The Axe-Fx III input was designed to mimic a typical tube amp input using an average of Marshall and Fender amps for the component values.
[50] The front and rear Input 1 share common circuitry.
FM9:
[51] The instrument input max voltage is about +/- 5.9V (11.8Vpp = about 17.5 dBu). Inputs 2/3 can handle up to around 11V (about 23 dBu).
[52] The SNR is dictated by the converters, not the source. You want as hot a signal as possible into the converters for best SNR.
- The noise floor of an A/D is fixed. For example the Cirrus Logic converters we use have a dynamic range of 114dB. That means the noise is down 114dB relative to full-scale.
- You only get 114dB of dynamic range if the input to the converter is at the voltage which generates a full-scale output.
- For every dB that the input is below that voltage the dynamic range decreases by the same amount.
- If your input to the A/D is 20dB below full-scale then your dynamic range drops to 94dB for the aforementioned converters.
- Therefore you want to drive the A/D with as hot a signal as possible (without clipping) to get the best dynamic range (least noise).
The same holds true for a D/A converter. To get the lowest noise from a D/A converter you want to run it as "hot" as possible. Now, the difficulty here is that running the D/A hot can generate a large output signal. So what we do is give you the Boost/Pad control (on outputs 3 and 4). The Boost/Pad control boosts the digital signal by XdB and reduces the analog gain after by the same amount. This allows flexibility in the outputs. If you need a hot signal for driving a power amp you set the Boost/Pad to 0dB. If you need a lower signal for interfacing with effect pedals you can reduce the output level.
For example, if you are interfacing to stomp boxes the typical maximum signal that a stomp box can handle is about 3V. However, the outputs of the Axe-Fx III can drive about 12V. If you set the Boost/Pad to 12dB the maximum output is now 3V and your noise is reduced by 12dB.
[54] The front and rear inputs are identical except the front input has variable input impedance. The SNR and dynamic range are identical.
[55] Fractal Audio products can handle 20dBu on their inputs as well (the instrument input range is 6dB less).
[56] Our products can output 20Vp-p. Likewise the inputs can handle up to 20Vp-p.
Instrument input: Secret Sauce
The instrument inputs on the amp modelers feature Secret Sauce
. On the Axe-Fx III this applies also to the rear input. This lowers the noise floor using a proprietary technique along with special analog input circuitry. The Axe-Fx III, FM3 and FM9 provide Secret Sauce version IV
circuitry.
FRACTAL AUDIO QUOTES
[57] The "Special Sauce III" uses a combination of things to get a lower noise floor. One of these things is new, premium Burr-Brown op-amps in the signal path which have extremely low noise and distortion (and are very expensive). As always I don't design stuff to be cheap, I design it to be good.
[58] The II and III don't use pre/de-emphasis.
PREVIOUS GENERATIONS
You have to set the input selection to match the input you're using. If you're using the front input then you must set the input selection to front and vice-versa. If you plug something into the front and set the input selection to rear it will get MUCH brighter. The front input is optimized for guitar level inputs and has spectral shaping and more gain than the rear input. The front input is optimized for guitar pickups. This is a combination of hardware and software processing. If you set the input source to Analog Rear this turns off the software processing part. If you are plugged into the front it will change the tone since you're still going through the hardware processing. This is why I say you must match the input selection to the input you are using. The rear inputs are standard line-level inputs and can be used with any program material. The front input, as stated above, is optimized for guitar pickups. As such it has more gain and less headroom and may clip if used for non-guitar program material. If you plug a guitar directly into the rear you may find you don't have enough signal level.
[59] You won't lose the "secret sauce" by putting a pedal in front.
Input Impedance
The inputs on the Axe-Fx II, the Axe-Fx III (front only), FM9, VP4 (L/Mono only) and FX8 feature adjustable/variable input impedance on the instrument input.
On the FM3 and AX8, input impedance is fixed at 1M ohm.
See Input impedance
for more information.
Inputs 2, 3 and 4
Input 2 on all devices is a LINE level port. It does not support the Secret Sauce
and does not support variable input impedance.
- Axe-Fx III
- Combi port (XLR + 1/4”). These ports support high-impedance sources such as guitars and basses, besides other gear. Because of this, there will be some white noise when Input 2 is connected to an output and nothing is plugged into Input 2 (this does not apply to ports 3 and 4). The signal-to-noise ratio is adjusted through Setup > Input > Input Trim. You can choose between mono or stereo input in Setup > Input 2 Mode. Use the Input 2 block on the grid to handle the input signal.
- The Axe-Fx III and FM9 provide additional inputs. Read I/O 3 and 4 for more information.
- FM9
- 1/4” port, L/R, balanced, line level. It can be used to connect an instrument. The signal-to-noise ratio and Boost/Pad can be fine-tuned in SETUP. You can choose between mono or stereo input in SETUP. Use the Input 2 block on the grid to handle the input signal.
- FM3
- 1/4” port, L/R, balanced, line level, designed for unity gain. It can be used to connect an instrument. The signal-to-noise ratio and Boost/Pad can be fine-tuned, and you can choose between mono or stereo input in SETUP. Use the Input 2 block on the grid to handle the input signal.
- For more information see Output 2 above.
- Axe-Fx II and AX8
- 1/4” port
FRACTAL AUDIO QUOTES
Axe-FX III:
[60] We wanted Input 2 to be able to support both line level sources and instruments. A guitar needs a very high impedance input impedance (1 Mohm). Line level sources typically see input impedances around 10K but work just fine at higher impedances.
The self-noise of a resistor is proportional to the resistance. Therefore a 1M resistor will have 100 times the noise power (20 dB!). However the input resistance is shunted by the source resistance so it effectively doesn't contribute to the noise figure.
A combi-jack does not have a shorting contact on the 1/4" tip contact like a regular 1/4" jack. The whole reason a regular 1/4" jack has a shorting contact is to short the input to ground when nothing is plugged in. This shorts the noise of the input resistance to ground. Without that shorting contact and nothing plugged in you get the noise of that input resistance and since it's 1M it's significant. Plug something in and the noise will go away. Or simply don't use it with nothing plugged in.
As a combo switch, its Input doesn’t get shorted to ground when there’s nothing plugged in, which means it’s left floating, which means it’s susceptible to noise.
[61] Input 2 isn't noisier. It doesn't have a "normaling contact" though so if you don't plug anything in it will be noisy. Plug something into it.
[62] Input 2 jacks are not "normaled" because the combi-jacks do not have normaling contacts. With nothing plugged in the input impedance is extremely high because they are designed to also be used for instrument inputs. You're not hearing distortion, you're hearing noise, which is normal because there is nothing plugged in.
FM9:
[63] The instrument input max voltage is about +/- 5.9V (11.8Vpp = about 17.5 dBu). Inputs 2/3 can handle up to around 11V (about 23 dBu).
Switching between guitars
When switching between guitars, there will be differences in level and tone just like with a traditional amp. There are several ways possible to handle this:
- Create separate presets for each guitar.
- Use different Input ports/blocks for each guitar, assigning each its own signal chain. Use the Multiplexer block to switch between them.
- Adjust Output Level in the Input block. This controls the loudness of the signal entering the grid. Use a channel for each guitar. Or, on the Axe-FX only, set it up as a Global block. Or, attach Output Level to an external controller and adjust the value through External Controller Initial Value in Setup > MIDI/Remote, or with a switch.
- Adjust Input 1 Gain in Setup > Global.
- Set up channels in the Amp block for different guitars, using different values for Input Trim for example.
- Attach a modifier to Input Trim in the Amp block, connected to a pedal or switch.
- Use the Neutral Input Boost function in the Amp block.
- On an Axe-Fx or FM9, use a different Amp block for each guitar.
- Use scenes and scene controllers, attached to Input Trim in the Amp block for example.
- Add a PEQ or Filter at the start of each preset and set its output level as desired. On the Axe-Fx only, set it up as a Global block. Or, attach its Bypass to an external controller and adjust the value through External Controller Initial Value in Setup > MIDI/Remote, or with a switch.
The Scene ignore feature also lets you adapt a preset to use with multiple guitars:
- Put a Filter block for example before the Amp block in your preset. Or put the Filter after the Amp block if you prefer that, or use a PEQ/GEQ, etc.
- Dial in the block level to match your low-output guitars with your high-output guitars.
- Turn on Scene Ignore on the Filter's channel.
- Assign a switch on your floorboard to Filter.
- When switching from a high-output to a low-output guitar, just turn on the Filter block. The Filter block will stay engaged when switching between scenes, regardless of its previously saved state in that scene and regardless of the Scene Revert setting.
Read section 4 of the Axe-Fx III and FM9 Owner's Manuals for an example preset for a dual output guitar, such as magnetic + piezo.
Multiple simultaneous instruments
- Axe-Fx III
- Guitar 1 connects to the Instrument input on the front or rear panels. Guitar 2 connects to Input 2, 3 or 4. Even a third and fourth instrument can be connected, and each can have its own signal chain on the grid, and its own output if desired. There are two Amp blocks, so two instruments can make use of amp modeling.
- FM9
- Guitar 1 connects to the Instrument input on the front or rear panels. Guitar 2 connects to Input 2 or 3. Even a third instrument can be connected. Each can have its own signal chain on the grid, and its own output if desired. There are two Amp blocks, so two instruments can make use of amp modeling.
- FM3
- Guitar 1 connects to the Instrument input at the rear. Guitar 2 connects to Input 2. Each can have its own signal chain on the grid, and its own output if desired. There's a single Amp block, so be creative.
For the above units you don't need an Amp block for an acoustic guitar, piezo or an electric that should sound like an acoustic, and perhaps not for bass with the help of the B7K drive model. You may even get away with a Drive block and a Cab block for clean guitar tones at the cost of dynamics. See Section 4 in their respective manuals for more information.
- Axe-Fx II
- Set Input 1 to Stereo. Connect one instrument to the front, and the other to Input 1 Right at the rear. Use two rows on the grid. Add a VOL block to each row. Set one to Input left for the instrument that goes into the front input or rear input 1 Left, and the other to Input Right for the instrument that goes into rear Input 1 Right. Add an Amp block after each VOL block if necessary. You can also leave out the VOL blocks and set Amp 1 to Input Left, and Amp 2 to Input Right; this only works with the Amp blocks in the first column. Continue the rows to the end, adding a CAB and effects to each one if necessary, or merge them if desired. Keep the signals separated by using the Balance controls.
- AX8
- To use the AX8 with three devices, guitar and two other devices such as piezo or synth, add an Amp and Cab. Put the FX Loop block after the Cab block. This sends the regular guitar sound to Output 2, and lets left and right signals from Input 2 enter the grid. Split the signal after the FX Loop block into two rows, and add a Volume block to each one. Set Input Select in one Volume block to Right Only. Set Pan and Balance as desired. Set Input Select in the other Volume block to Left Only. Set Pan and Balance as desired.
For more information see these pages:
- Fractal Audio's forum: “AX8 - Can this be done?”
- YouTube: “How-to play 2 Guitars with 1 Axe-FX II (With FX-LOOP)”
Acoustic instruments
An acoustic instrument with a pickup can be connected to the modeler.
An impulse response (IR) of an acoustic body can add realistic acoustic resonance to the tone, or use the Resonator block if available on the device. Try to use UltraRes IRs when using acoustic IRs when available, but there are no acoustic IRs among the factory cabs. You can find some on Axe-Change.
A basic preset for an acoustic guitar will normally suffice. Use some compression, EQ and reverb, but an Amp block is not required, although the TUBE PRE Amp model can be used to warm up the tone.
You can also use Tone Matching with great results.
Watch the video below.
Read the Owners Manuals for the Axe-Fx III, FM9 and FM3 for setup suggestions.
Bass guitar
The modelers provide bass amp models and built-in IRs of bass cabinets.
The tuner supports bass guitar tuning. The Axe-Fx III, FM9 and FM3 feature improved pitch detection for bass guitars.
The factory preset FILTERING FUNK has a scene Faux Bass
which turns an electric guitar into a bass.
For more information see these pages:
- Fractal Audio's forum:
Bass & Other Instruments
- Talk Bass.com:
Fractal Audio (FAS) Axe-Fx 2 - thoughts, ideas, and use - input welcome! (long read)
- YouTube:
Axe FX bass guitar tone tutorial (pop & rock/metal)
- Leon Todd's videos on YouTube:
Leon Todd's tutorials
MIDI Guitar
See the Axe-Fx III -> Guitar 2 Midi - full guitar synth without hardware!
discussion in the Fractal Audio forum.
External effects
External effects, such as pedals, can be integrated into a Fractal Audio-based rig in several ways:
- Between guitar and processor
- If you want to connect an effects pedal to an amp modeler, with the processor configured for Amp and Cab modeling, connect it between the guitar and the instrument input on the processor. Remember to check the Input impedance (AX8 and FM3: n/a), and make sure the pedal's output doesn't overload the input of the unit.
- Effects loop
- Alternatively, insert the effect in an effects loop. Make sure to adjust levels where needed (block(s), I/O menu, output level knob on front/top panel. You can include/exclude the effect per scene, or use the effects loop block as an audio switcher. On the Axe-Fx III, FM9, FM3 and AX8, set the Output knob to its maximum position to achieve unity gain, and use the Boost/Pad parameter in SETUP for the used Input port to set the optimal level for low noise floor.
Output 2 on the FM3 is designed for unity gain applications, like Outputs 3 and 4 on the Axe-Fx III. In a unity gain setup, i.e. when adding an external effects pedal to the FM3, keep the Output 2 block connected to the Input 2 block. IN 2 is specially designed to work as a bypass for the entire loop, allowing signal to flow from In 1 to Out 1 even when the outboard gear is not in use.
For more information read:
Setting up an effects loop on the Axe-Fx III
Connecting external gear before and after the Amp on the FM3
FRACTAL AUDIO QUOTES
Axe-Fx III:
[64] The input can handle up to +/- 5V which is greater than any 9V pedal can deliver.
[65] 16dBu is approx. 7V peak.
[66] The outputs have adjustable pads.
PREVIOUS GENERATIONS
Axe-Fx II:
[67] The input buffer is designed for ~10Vpp max.
Wireless receiver
A wireless receiver can be connected to the instrument input or another input.
When using the Axe-Fx III, connect the wireless to the rear instrument input. If you want or need to use a cable plug it into the front input and it will override the rear-panel input automatically.
Be aware that adding a digital wireless system will add some latency to the signal.
FRACTAL AUDIO QUOTES
[68] A wireless will add noise. It's physics. Nothing you can do about it.
PREVIOUS GENERATIONS
Axe-Fx II:
[69] The front input has a better SNR but if you are using a wireless the better SNR of the front input won't be noticeable since the noise of the wireless will dominate.
Microphone
A microphone should be connected to a LINE input. That's Input 2 on the Axe-Fx II, AX8 and FM3, Input 2, 3 or 4 on the Axe-Fx III, Input 2 or 3 on the FM9 or Input 2 on the FM3.
The hardware does not have built-in microphone preamps, so there will be a level mismatch between the line level input and the microphone's output level and the microphone's signal may be too low. Increasing its signal on the grid works but may add noise.
A better solution is to increase the level of the source to get sufficient signal strength into the unit by using an external mic preamp or a device like Shure's A85F adapter, which keeps noise low.
The Cab block's Preamp page lets you add virtual mic preamp distortion, if needed.
Bluetooth not supported
Fractal Audio devices do not provide built-in support for Bluetooth connections.
FRACTAL AUDIO QUOTES
Bluetooth latency is ~40ms. That would be intolerable.
Levels
About levels in the Axe-Fx III, FM3 and FM9
The following was first published in the forum in Everything you've always wanted to know about LEVELS (III, FM3, FM9)
:
Introduction
The Axe-Fx III, FM3 and FM9 provide parameters at various places that control the level of the signal directly, as well as meters that display levels visually. This applies to the hardware and software. This document explains them, following the flow of the signal.
Hardware A/D Sensitivity Levels
- The guitar's output signal enters the hardware through the instrument input. The first parameter that matters, is found at Setup : I/O : Input. The A/D Sensitivity parameters control the signal going into the analog-to-digital converter. Setting it correctly makes sure that minimal undesirable noise will enter the processor (aka signal-to-noise ratio or SNR).
- The FM3 does not have these parameters. Instead, it provides Setup : I/O : Audio : Input Pad parameters.
- The INPUT LEDs on the hardware correspond with these parameters.
- Setting the parameters correctly means that the meter in Setup : I/O : Input doesn't go into red and there doesn't appear a warning about clipping. It’s common for some guitars not to hit red at all, which is nothing to worry about. If you have multiple guitars, just set the parameter for the loudest one, and leave it there. There’s 6 dB of headroom left when the hardware LED goes into red. There's 0.5 headroom left when the warning about clipping appears on screen.
- IMPORTANT! The A/D parameters do NOT affect volume, tone or the amount of amp gain. That’s because the processor compensates.
- When you page right from the Home menu, you reach the Meters page. The ANALOG IN meters show the same thing as the INPUT LEDs on the hardware, without the green / orange / red colors.
- After the A/D conversion, the signal (the note or chord you struck on your guitar) is now in the so-called digital domain.
Digital Audio Input
Setup : I/O : USB/AES provides level controls for signal entering the processor through USB channels and (on the Axe-Fx III only) SPDIF and AES. Check these if you're connected to a computer and you get no sound from your DAW, YouTube, etc.
Input 1 Gain
The Axe-Fx III provides a parameter to adjust ALL presets for variations in guitar output level: Setup : I/O : Input : Input 1 Gain. It trims the level of Input 1 before the start of the grid so, unlike the A/D Input Level parameters, it has an impact on blocks such as the virtual amplifier.
On the Axe-Fx III and FM9, this parameter is located in Setup > I/O. On the FM3, it's in the Global Settings.
Preset: Input block
The signal enters the layout grid through an Input block. Like all blocks on the grid, it has a level parameter and 4 channels. This parameter lends itself well to adjust the signal for differences between guitars per preset, as an alternative to the global Input 1 Gain parameter mentioned above.
Preset: Amp block
- When it comes to levels, the Amp block on the grid is special. People often use the Amp Level parameter to set the overall level of the preset. This parameter controls the output of the Amp block and therefore does not affect the gain or tone of the virtual amplifier.
- The Amp block also has a level parameter at the input of the Amp block: Input Trim. It can be used to mimic the difference between the Low and High inputs on a real amplifier, or to control the virtual amplifier’s gain (instead of using Gain in the Amp block).
- There's much more to the Amp block, like Master Volume, but that's beyond the scope of this article. More information
Preset: More about blocks
- When you select a block on the hardware and press Edit, you’ll see a mini meter, indicating the left/right input resp. output signals. The software editors do not provide these mini meters. If the input mini meter hits red, it means that the output level of the preceding block is too hot. Blocks in the digital domain can’t really clip though; that can only happen at the final digital-to-analog conversion stage.
- Page right on the Layout screen to reach the Meters page (not the same as the Meters page on the Home screen), and you’ll see those mini meters for the entire grid. These are very handy to detect the cause of routing or level problems!
- It’s good practice to aim for unity gain where possible, meaning that engaging and bypassing a block should not cause the sound to get softer or louder, unless that’s the goal.
Preset: Output block
- The signal exits the layout grid through an Output block. While the Amp Level parameter is the main parameter to control the overall preset level, Output Level can also be used as such. Especially because it provides additional functionality.
- First, it lets you set individual output levels for each of the 8 scenes of the preset. Handy if you prefer to use dedicated scenes for soloing and such, but note that changing the output levels of individual scenes also affects the level of reverb and delay trails when switching between scenes, which may be undesirable.
- Also, it provides meters that display the very important preset output level.
Preset: Level Meters
- As written above, the Output blocks on the grid show vertical meters that display the final preset output level.
- The same meters, but now displayed horizontally, appear when looking at the Layout screen in “zoomed out” view. These are often referred to as VU meters which show the relative loudness of the preset.
- The software editors show the same meters in the Preset Leveling window.
- These meters, which all show the same thing, can be used to set and match the levels of presets for consistent sound. Ideally, the level of the preset should hover around the red lines in the meters. The VU meters are calibrated such that there is still 12 dB of headroom at the red line with the OUT knob (see below) at maximum.
Global EQ
Each Global EQ, found in SETUP, includes a level parameter. This lets you control the overall level of the outgoing signal through that particular output port. This does not affect AES, SPDIF and USB Audio.
Hardware OUT knobs
- Finally, the OUT knobs on the hardware let you adjust the overall volume for each pair of analog outputs. The exact position of the OUT knobs is shown as a percentage in Setup : Utility : ADC Levels.
- OUT 1 also controls the volume level of the headphones output.
- These knobs do not affect the USB Audio, SPDIF and AES output levels.
- The OUTPUT LEDs on the Axe-Fx III show the digital levels going into the D/A converters. The FM3 and FM9 have a red CLIP LED instead of meters.
- When the LED(s) indicates output clipping, there are two ways to intervene: (1) adjust the preset output level (on the grid or with the Global EQ level) or (2) turn down the OUT knob. Because together they set the level into the D/A converter. Note that output clipping can’t damage the device.
- When you page right from the Home menu, you reach the Meters page. The ANALOG OUTPUT meters show the same thing as the OUTPUT LEDs on the hardware, but without the green / orange / red colors.
- The maximum output level of the Axe-Fx III, FM3 and FM9 is around 22 dBu.
Nominal Output Level
Setup : Audio : Output Level lets you choose between -10 and +4 for the XLR outputs. This is the overall nominal output level. The default is -10 dBv to reduce the number of support cases due to people overloading the inputs on consumer-grade interfaces, mixers, etc. Most professional gear runs at +4 dBu so you may want to change the level to +4 dBu in that case. The legacy Axe-Fx II is set to +4 dBu at default, so it is louder at factory settings.
Downstream Gear
Powered monitors, amplifiers etc. provide levels controls of their own. This is beyond the scope of this article.
I/O Loops
I/O ports 3 and 4 on the Axe-Fx III, I/O port 2 on the FM3, and I/O 3 on the FM9, are designed for unity gain applications, such as effect loops. What comes in, goes out at the same level. To achieve this, turn the corresponding OUT knob fully clockwise.
A final word...
A level parameter is just that. It makes the signal louder or softer. It's digital, it has no sound of its own, it's neutral. Changing the value of a block’s level parameter will only change the sound (gain, distortion, tone, etc.) when that block is followed by non-LTI effects such as an Amp or Drive block.
Main input level

- Axe-Fx III – I/O > Input
- FM3 – I/O > Audio
- FM9 – I/O > Audio
- VP4 – Audio
- Axe-Fx II – I/O > Input > Instr In/Input 1/Input 2
- AX8 – I/O > Levels > IN 1 (Instrument) Pad/In 2 (Fx Rtn) Nominal Level
- FX8 – I/O > Levels > Input 1 (Pre) Pad
- What is Input Level or Input Pad for?
Input Sensitivity, on the Axe-Fx III and FM9, and Input Pad on the FM3 and VP4, are NOT gain controls. They do NOT affect the overall volume level, they have no effect on output clipping or on amp gain. The control only optimizes the signal-to-noise ratio (sensitivity) of the analog-to-digital converters. The adjustment is applied before the A/D converter and is offset by a corresponding but opposite boost at the output of the converter.
FRACTAL AUDIO QUOTES
Axe-Fx III:
[70] The inputs can handle up to +18dBu. Use the Input Sensitivity controls to adjust accordingly.
FM9:
[71] The instrument input max voltage is about +/- 5.9V (11.8Vpp = about 17.5 dBu).
Inputs 2/3 can handle up to around 11V (about 23 dBu).
If you need to set it to 5% then set it to 5%. Don't worry about it seeming low. It's just because it's a linear control.
- How to set Input Sensitivity or Input Pad
- Set it below the point where the signal start clipping. Watch the meter. Make sure to strum hard, on the loudest pickup. Don't worry if you can't make the warning appear at all, that DOES NOT have an impact on tone or gain. If you have multiple guitars, just set the parameter for the loudest one, and leave it there.
- There’s 6 dB of headroom left when the hardware LED goes into red. There's 0.5 headroom left when the warning about clipping appears on screen.
- FM3, AX8 and FX8
- These units let you choose from fixed input padding settings. A higher Input Pad value means lower input level ("padding"), which increases noise floor. So keep the pad as close to 0dB as possible.
FRACTAL AUDIO QUOTES
FM3:
[72] The pad set to 18 dB is equivalent to setting the Input 1/Instr A/D Input Level to 10% on the Axe-Fx III.
- VP4
- The VP4 lets you choose from fixed input padding settings. The Input Pad setting can be adjusted from 0 dB (for low-level input signals) to 6 dB, 12 dB, or 18 dB (for progressively louder input signals). The default Input Pad setting is 12 dB, which is ideal for guitars with hot pickups.
- When the input clips, the words “IN CLIP” also appear in red in the title bar of the main display, indicating the need to increase the pad setting.
- If the input of the VP4 clips persistently, the unit will automatically increase the Input Pad setting. When this occurs, the word “Auto” will appear next to the Input Pad value, for example: “12 dB (Auto)” indicating that the pad was automatically increased to 12 dB. When you reboot the VP4, the automatic setting is cleared, and the last manually selected value is restored. If you want to make the automatic pad setting permanent, just turn the Input Pad knob one “click” to clear “Auto” and set the desired value. While "4CM Routing" is enabled, a common input pad setting is shared by both PRE and POST inputs. Excessive levels at either of these will cause the automatic pad setting to be applied to both.
- If the input still clips with the pad setting at 18dB, decrease the output level of the device(s) connected to the VP4 input(s).
- Axe-Fx III and FM9
- The Instrument input on the Axe-Fx III is more sensitive than the Axe-Fx II's, but it has more headroom/dynamic range.
- When using a mono instrument, do not set the Input Mode to Stereo or Sum L+R. Select Left Only (default), otherwise the level will be attenuated.
- Input levels can be also controlled via MIDI CCs.
- Firmware 22+ for the Axe-Fx III include an on-screen warning about input clipping (within 0.5 dB of full-scale), because signal peaks can clip the signal, even when the Input LED meter doesn't reach the red LED. There warning is reflected in the mini-tuners (going red) and the meter under Input 1 Level/Instrument in Setup > I/O > Audio.
FRACTAL AUDIO QUOTES
[73] For a Strat, near 100% on the input level is not unusual. I run my Strat around there. It has vintage-type pickups.
[74] To get the best noise performance it is important that the Instr In trim is set correctly in the I/O->Input menu. Set this as high as possible without clipping the input.
[75] You don't HAVE to tickle the reds. Adjust for your hottest guitar and leave it.
[76] The AFXII has digitally controlled potentiometers before and after the A/D and D/A converters. Therefore it knows what the input and output gains are. It compensates for these gains in the digital path.
Full-scale is a term that indicates the maximum signal level into or out of an A/D or D/A converter, respectively. With digital converters the best performance is achieved by operating the converter such that the nominal signal level is close to full-scale. The exact voltage is unknown and irrelevant. Most digital gear will have indicators that measure the levels relative to the converter's full-scale value. For example, the input meters on the Axe-Fx indicate the input signal relative to the A/D converter's full-scale value.
[77] There is no single optimum setting. If you have hot pickups with thick strings and a heavy hand you may need to set it at 10% or less. If you have vintage single-coils with thin strings and a light touch, 100%.
[78] The inputs can handle up to +18dBu. Use the Input Sensitivity controls to adjust accordingly.
[79] Many things contribute: number of windings, magnet strength, distance from strings, string type and gauge, pick thickness, how hard you pick, etc.
Nothing has changed in the input processing. The clip indicator trips when the input is within 0.5 dB of full-scale. If if trips you should turn down the sensitivity.
FM3:
[80] Input dynamic range has everything to do with the ability to handle low level signals. The normalized gain of even a medium gain tube amp can be over 60 dB. If your input dynamic range is only 96 dB and you leave 6 dB of headroom your noise floor is now a paltry -30 dB. There's a reason modeling products use various techniques to improve input dynamic range including dual-range A/D techniques, channel doubling, companding, pre/de-emphasis, etc.
Algorithms are extremely important. However usually the quality of the algorithm is proportional to its complexity. The higher the complexity the more powerful the processor required. One of the main reasons today's modelers sound so much better than they did just a decade ago is the increase in computing power allowing more advanced algorithms.
Axe-Fx II:
[81] The Input Trim control in the I/O menu is before the A/D. You can use that to reduce the level into the A/D.
[...]
If you want 4 dB of gain reduction:
A = 10^(-4/20) = 0.63
So you need to reduce your input pad by 37%. The new value is 0.243 * 0.63 = 0.153 => 15.3%Input 1 is normalized to 1V. The other inputs are normalized to 8V. 20 * log10(8) = 18 dB.
OTHER QUOTES
Cooper Carter:
[82] […] The Instrument Level is to make it so the A/D converter hears the best signal it possibly can. So say you have a super low output Strat. You crank up the input level so that that Strat is hitting the converter at a level that is making sure it's well above the (very low) noise floor of the Axe-Fx. The A/D does its work and then brings down the signal it outputs to the processor by the same amount you gained up, so that what is coming in is going out, regardless. Conversely, if you have a super hot guitar, like an EBMM JP15, it's already hitting the A/D way above the noise floor, and you don't want to add unnecessary noise by having the input higher than it needs to be to convert the signal at an optimal level. So you turn the input level down a good bit. The converter then compensates for how much you turned down by bringing up the signal by an equal amount before it outputs to the processor. The signal hitting your grid (i.e. pedals, amps, whatever) is in theory unchanged in level from what is coming out of your guitar. You've just optimized the level at which it's being A/D converted.
You "can't" really "clip" the input given that it takes drive pedals and what-have-you just as well as an amp does.
Main output level

The main output levels on the amp modelers are directly controlled with the hardware output level knobs, and also depend on system settings and preset settings.
- Axe-Fx III and FM9
- The default nominal output level of Outputs 1 and 2 is -10dBV. It's adjustable: -10 or +4 (Output 3 and 4: n/a). The red LEDs on the front panel come on at -1 dBFS, which differs from previous hardware. A front panel LED meter bridge provides instant visual status for the inputs and (analog) outputs. A Meters page in the Home menu and layout grid also shows I/O levels. The Output blocks also provide meters (same as VU meters). Finally, the Utility lets you check the performance of all four outputs.
- FM3
- The default nominal output level of Output 1 is -10dBV. It's adjustable: -10 or +4 (Output 2: n/a). The red LEDs on the top panel come on at -1 dBFS. A front panel LED meter bridge provides instant visual status. A Meters page in the Home menu and layout grid also shows I/O levels. The Output blocks also provide meters (same as VU meters). Finally, the Utility menu lets you check the performance of all outputs.
If you need to set the output level of the Axe-Fx III or the FM3 to an exact value (like on the Axe-Fx II), use the Utility > ADC Levels menu.
If you are clipping the outputs, you need to lower the level INSIDE your presets. The physical OUT knobs come after the converters and only affect the level of what you hear.
There's NO need to put a DI box inbetween the modeler's output and the mixing board.
MIDI CCs can control output levels. To reset them without the help of a MIDI controller, change the assignment to "NONE" in I/O.
The main output level is affected by the output level of the selected preset, and the Global EQ's Gain control.
- VP4
- Max output level is 16 dBu.
- Axe-Fx II and AX8
- The nominal level of the main outputs defaults to +4dBu line level (adjustable on the AX8). This means that you should connect the Axe-Fx II and AX8 to a LINE level input on the mixing board, when available, because the output signal is too hot for a MIC input. If only MIC inputs are available on the mixing console, try this:
- Use a pad switch on the mixer to attenuate the signal and prevent clipping
- Decrease input gain on the channel strip
- Decrease the output level from the device by turning down the Output knob at the front.
FRACTAL AUDIO QUOTES
[83] The converters are AFTER the output level knobs so you may be clipping when converting to fixed-point for USB but the converters won't clip if the output level knobs aren't all the way up.
[84] -10 dBV is compatible with instrument levels.
[85] The default Output Level for Output 1 and 2 is -10 dBv. This was done to reduce the number of support cases due to people overloading the inputs on consumer-grade interfaces, mixers, etc. (IOW cheap stuff). Most professional gear runs at +4 dBu so if using a pro-grade interface, mixer, etc. you may want to go into the Global menu and change the level to +4 dBu.
[86] The Axe-Fx III maximum output level is over 22 dBu (!). The VU meters are calibrated to -12 dBFS. So at the zero line on the VU meters and with the output level knob all the way up you would be putting out around 10 dBu. That's enough to drive any power amp, and then some. The typical power amp has an input sensitivity of 0 dBu for full power so there's more than enough oomph there.
[87] +4 dBu is the nominal output. Max output is +20 dBu.
[88] The meters on the front panel are the post-fader meters.
[89] The meters in the (Output) block are pre-fader (Level knobs on front of unit). The LEDs are post-fader. Simple as that.
[90] The meters on the front of the Axe-Fx are relative to full-scale. They are not calibrated in dBu. They are to assist you so that you don't clip the converters.
[91] The front panel meters indicate the level INTO the D/A converters. The only place the system can clip is at the converters so the meters let you know when you are in danger of clipping the converters.
[…] A signal is generated internally. That signal can be any value from 0 (negative infinity dB) to a thousand dB, in theory. That signal is then multiplied by the "gain" of the output level knob (0 to 1). The knobs have an audio taper but that's irrelevant. If, after applying that gain, the signal exceeds 1.0 the converters will clip and red LEDs on the meters will light.
If you think about the meters as level into the converters it all makes sense because that's what it is. To further demonstrate this increase the Boost/Pad setting for Output 3/4 and watch what happens.
The output meters are the analog of the input meters. They indicate converter levels. Nothing more, nothing less. And what they do is extremely important and convenient.
All Fractal Audio products use floating-point processing. In fact the Axe-Fx III uses 64-bit floating-point in many places. It's impossible to clip internally. The AX-8 and Axe-Fx II use 40-bit in many places and are also impossible to clip internally.
FM3:
[92] The maximum output level is around +22 dBu.
[93] FX III is 6 dB higher than FM3 on Output 1.
[94] If you are clipping the output, which is the final fixed-point signal to the converters (all audio converters use fixed-point), then your internal signals are far too high. If you use the VU meters and set your output to 0 dB, you are guaranteed 12dB of headroom at the converters with the output level knob all the way up. I've never witnessed a palm mute that was more than a few dB hotter than nominal.
Go into the Layout menu and press the Zoom hotkey. This will display VU meters for the two main outputs. Adjust the level of the Amp block (using the Block Level knob with the Amp block selected) so that the signal hovers around the 0 dB marker. If you do this it's impossible to clip the outputs.
The factory presets are all adjusted for roughly 0 dB on the VU meters. Even with the output level knob all the way up I never get anywhere even close to clipping.
We could've taken a conservative approach and built in a lot of headroom so that clipping the converters was impossible but then you lose dynamic range. The approach taken optimizes the dynamic range of the converters (so you aren't wasting bits) thereby ensuring maximum fidelity and lowest noise. It does require that the user adjust their presets correctly to avoid overflowing the converters but the VU meters make this task trivially easy.
[95] It's impossible to clip internally. The output block level meters are intended for use in leveling presets. When routing a signal from Input 1 to Ouput 3 or 4 it's entirely possible for the meters to enter the red zone. This is not an issue. The only place clipping can occur is at the final D/A stage which is indicated by the front panel meter bridge. If the red LEDs light then the D/A is clipping.
[96] […] Brief excursions into clipping may not light the clip LED long enough to be noticeable but can be audible. There is a hard limiter prior to D/A conversion that prevents wrap-around but if your preset is too hot you can hit that limiter which will sound nasty.
As a rule of thumb, a preset shouldn't clip regardless of the pickups used. If you plug in a hotter guitar and the output clips, then your amp block output level is too high.
Axe-Fx II and AX8:
The XLR output is balanced but it's +4dBu nominal. The problem is people connect it to a mic input which is way too sensitive for that level signal. If the board has a mic/line switch you want to set it to line level. Or if it has a pad switch turn that on. Otherwise turn the level knob way down. The thing to remember is that XLR is just a connector. It doesn't imply microphone levels. Most pro stuff like eq's, etc. have line-level XLR's.
AX8:
[97] The output doesn't go all the way to zero. This was done due to the plethora of support issues where people would say they weren't getting any sound and it was simply due to the fact that they had the knob turned all the way down. So now you get a little signal and we get less support calls.
Axe-Fx II:
[98] We test the output to be flat within +/- 1 dB over the range of the knob. In fact I'd be surprised if there were any measurable variation at all.
[99] The output "pot" is actually a ladder of discrete resistors that is remotely controlled by the knob on the front panel. Other products simply reduce the digital signal going into the D/A converter but this is sub-optimum as you reduce your dynamic range when doing this. The Axe-Fx II strives to keep the signal into the D/A as high as possible for optimum dynamic range and then controls the output level using a programmable output gain. The downside of this approach is that you will hear a small noise when the output switches between the resistors in the ladder.
[100] To place a pot after D/A requires running cables to/from the front panel. These cables can degrade signal quality and pick up noise. The pots on the front panel of the II are remote controls for the digital pots. The signal never passes through them. The digital pots also allow us to boost the level from the D/A and then attenuate it precisely to improve output SNR. The Output X Boost/Pad feature would be impossible without digital pots.
Axe-Fx II: (due to single-ended designs and low-voltage/low-power constraints)
Optimal gain staging would be with the level knob around noon. Higher than this and you risk clipping the inputs of the downstream device. With the level knob at full the Axe-Fx II will probably incinerate a Soundblaster or other low-cost stuff. The max level out of the Axe-Fx II is +20dBu. Most pro gear can easily handle that but lots of gear cannot and the trend in newer gear is towards lower and lower maximum input levels . In the old days, +20dBu was routine. Everything could put out and handle +20. Not so much anymore.
[101] The II actually has more output than the I. The II can do about +20 dBu, the I was about +18.
[102] Start with amp volume at noon. Bring up Axe-Fx volume until desired level is reached. If you need more, turn up amp. With the Axe-Fx volume all the way up you would be pushing +20 dBu into the amp which could clip the inputs to the amp.
Preset levels
Read Presets for more information
Headphones, In-Ear Monitoring (IEM)
Headphones
Routing
Use the Output 1 knob to set the headphones level. If you have both monitors and headphones connected and want to listen through headphones only, use one of these methods:
- Switch off the monitors.
- Connect the studio monitors to another output and send the Output 1 signal to that output in SETUP.
- Use a line level attenuator to turn down the monitors' level without affecting the headphones level.
If you have a Wet/Dry set up, and want to hear both through headphones or IEMs, send Dry through Out and Wet through Out, and combine those signals into OUT 1. See Route OUT2 to Headphones?
in the forum for an example.
To process incoming USB Audio signal before it is routed to an output, put the Input USB block on the grid, add effects, and add the Out block. To route it back to the computer, route the signal to Axe-Fx III USB outputs 7/8 in the computer.
FRACTAL AUDIO QUOTES
[103] Headphones are hardwired to Output 1.
That's a hardware connection. Phones will always match Out1.
For more information read GlennO's Axe-FX For The Recording Musician
in the forum.
Impedance and volume
If the volume level through your headphones is very low, switch to lower impedance headphones (such as 32 Ohm), use a headphone amp or use headphones with a built-in amplifier. The Axe-Fx III is better at feeding sufficient signal level to hard-to-drive headphones than the Axe-Fx II was.
Northwest Audio & Video Guy has the Headphone & Amp Impedance
article that is useful.
FRACTAL AUDIO QUOTES
[104] The headphone amp in the III is a pro-quality amp designed to drive low-impedance pro headphones. It's not designed for use with things like headphones with built-in amps and IEM amps.
[105] The Axe-Fx III headphone amp is excellent. There are likely dedicated headphone amps that are better but I would have to see the schematic to form an opinion. Many OTS headphone amps are nothing more than a cheap op-amp in a box.
IMO the best way to make a headphone amp is to use an op-amp and then add a current booster inside the feedback loop. You can use a complementary pair of transistors to do this.
No phones output
The AX8, early FM3 units and the VP4 do not have a dedicated output for headphones. Use a Y-cable with the outputs. If you connect your headphones directly to the AX8, you may get less signal level than from a dedicated headphones output on other devices. A popular solution is to use a small headphones amp, such as from M-Audio or Rolls.
FRACTAL AUDIO QUOTES
[106] It does not have a headphone output but the outputs should be able to drive phones with ease. You'd just need a Y-cable adapter.
[107] The output impedance of the 1/4" outputs is 600 ohms IIRC. This may be too high for some headphones. We always use a small output impedance on our designs to help protect the output devices against improper connections, ESD, etc. The outputs were not really designed to drive headphones, they are designed to drive high-impedance inputs (>10K). Headphones will work but it won't be optimum. For optimum results use a dedicated headphone amp.
Optimizing sound
Sound through headphones can be dull:
FRACTAL AUDIO QUOTES
[108] Because there's no string and body reinforcement. When you play through speakers the sound couples into the guitar body and strings. With headphones you don't get this so the sound is very sterile and lifeless.
Now, if you use speakers during recording and then playback through headphones it will sound fine.
[109] It's lack of acoustic reinforcement. I did a test a few years ago and I don't remember the actual numbers but having a speaker aimed at the guitar adds many dBs of power to the lower mids coming out of the guitar. IOW, if you measure the spectrum of the signal coming out of a guitar alone and then compare that to the signal coming out with a cab or monitor in proximity at a reasonable volume there are a LOT more lower mids with the speaker present. This results in a "thin" sound without the speaker.
[110] The problem with headphones is that there is no acoustic reinforcement of the guitar. There is zero coupling between the speakers (inside the headphones) and the guitar. Without that coupling, which is a type of positive feedback, the sound is lifeless, thin and harsh.
When your heroes recorded their guitar parts that weren't using headphones.
On "Appetite for Destruction" Slash recorded his guitar parts in the control room. To get even more coupling into the guitar a combo amp was in the control room with him pointed at the guitar. A volume pedal allowed him to adjust the volume of the combo amp so he could control the coupling. With the volume pedal all the way up he could get controlled feedback.
I've actually done tests comparing the spectrum out of the guitar when there is no coupling (i.e. monitors turned off) and with typical coupling (monitors loud or using a conventional cab). The boost in the low midrange is significant. I forget the actual numbers but it was at least several dB.
I did some studies years ago and having a speaker in proximity to the guitar actually changes the final tone considerably. I compared the frequency response with the amp in isolation to the frequency response with the amp in proximity and measured several dB difference in the lows and mids. It was clearly audible when the recordings were played back.
Tips for improving sound quality through headphones:
- Use FullRes IRs in the Cab block or IR Player block.
- Use a far-field Impulse responses (IR).
- Use a
correction EQ IR
to make your phones sound more flat. - Increase Proximity in the Cab block.
- Increase Room Level in the Cab block.
- Select the Ambience type in the Reverb block.
- Always use a stereo output signal.
- Add the Enhancer block to presets.
- Increase De-Phase / Smoothing in the Cab block.
- Use Gain Enhancer in the Amp block.
Avoid wireless headphones because they increase latency.
For more information see Wikipedia's Headphones
article.
In-Ear Monitoring (IEM)
In-Ear Monitoring (IEM) provides a way for musicians to monitor sound through earbuds, instead of floor wedges etc. While this provides a superior listening environment, it takes getting used to the direct sound into your ears and the absence of surround sounds.
The I/O architecture of the Axe-Fx III and FM make it easy to send and receive IEM-specific signals, without the need for an external mixer.
The same optimisation tips as for headphones apply, see above.
WARNING: Always use the built-in limiter of your IEM system to protect your ears against sudden spikes and peaks!
For more information see Cooper Carter's tips for dialing in IEMs
in the forum.
Full Range Flat Response amplification (FRFR)
See the rig diagrams in Section 4 of the Axe-Fx III, FM9 or FM3 Owner's Manual for many examples.
Why use FRFR monitoring
Listening to a virtual amp with a cabinet model requires an amplification system or listening device that covers a broad frequency spectrum, from 20Hz up to 20kHz, AND adds as little coloring of its own as possible. Those systems are called FRFR
, for Full Range Flat Response
, also referred to as neutral
because what goes in, comes out. Tone shaping is entirely left to the input device, which in this case is a Fractal Audio modeler.
From the Axe-Fx III Owner's Manual
A Full-Range Flat Response (“FRFR”) system aims to reproduce the entire audio spectrum without compromise. In comparison, most guitar speakers are narrow range, with no ability to accurately reproduce extended lows and highs. A 1×12 open-back combo is never going to sound like a 4×12 stack. In comparison, full-range flat response studio monitors, high‐quality PA speakers, and FRFR speakers designed specifically for guitar should be able to reproduce anything you play through them.
Many so-called FRFR devices really do not have an entirely flat frequency response.
Among the advantages of FRFR amplification:
- portability
- no tone coloring
- reduced stage volume
- consistent tone at all volume levels and in every venue
- flexibility of cab modeling
- good reproduction of synth and acoustic tones
- the musician hears exactly what the audience hears
For more information see:
- Wikipedia:
Full-range speaker
. - musicradar:
Modelling preamp systems and full-range, flat response cabs explained
Which systems are FRFR
FRFR systems include:
- Studio monitors.
- Active (powered) FRFR cabs and wedges.
- Passive FRFR cabs and wedges, powered by a separate neutral amplifier.
- High-quality headphones.
- High-quality P.A.
Popular manufacturers of FRFR solutions for stage use include Atomic, EAW, ElectroVoice, Friedman, Matrix, Meyer, Mission Engineering, QSC RCF, XiTone, and others.
Quality studio monitor brands include Focal, Adam, Genelec.
Close-miking
FRFR amplification leaves tone shaping entirely to the modeler. That includes the use of a virtual speaker AKA a cab model
. Fractal Audio's cab models are Impulse Responses (IRs
). These are sampled sounds of speaker cabinets, with the recording microphone(s) placed within inches of the speaker cap or cone (near-field
). This is referred to as close-miking
.
Compared to the sound of a traditional amp and guitar speaker, AKA in the room
or far-field
, close-miked sound has much more bass content, because of the microphone's proximity to the speaker when capturing the IR. Also, there is much more high-frequency content, because the recording mic usually is placed on-axis to the speaker's cap.
Becoming accustomed to the FRFR sound can take some time. Instead of listening to a traditional guitar speaker, you're hearing the sound of a close-mic'd speaker cabinet, because of the use of cabinet modeling. The directivity of an FRFR speaker is also different from a traditional guitar speaker.
See The One Thing Every Influential Guitar Tone Has In Common
on YouTube for more information.
FullRes
is Fractal Audio's proprietary technique of adding room to recorded guitar tones and sound through headphones.
For more information see:
Impulse responses (IR)
in the Wiki.- Wikipedia's
Microphone practice: Basic techniques
article.
FRACTAL AUDIO QUOTES
[111] You're never going to get a full-range monitor to sound like an amp in the room regardless of the IR used. One reason for this is dispersion. A traditional guitar cabinet has a beam pattern that decreases with increasing frequency. This means less high frequencies when listening off-axis. A full-range monitor will have more highs. Now some will argue that if you capture the traditional cab off-axis in the far field then you'll get the same thing but you won't because the monitor is not interacting with the environment in the same way. The traditional cab will send less frequency content to off-axis which is then reflected off the floor, walls and ceiling. The monitor will send more highs off-axis that are reflected. Our hearing relies a LOT on the spatial cues of reflection and the reflections will not be the same.
Compound the above with the fact that 99.9% of IRs are near field captures which sound nothing like the far field.
I believe trying to get a monitor to do amp in the room is a lesson in futility. If you really want that sound use a traditional guitar cab.
[112] You're not going to hear the same thing through FRFR that you heard from guitar cabs. Your audience will hear something very similar but you won't. What you're hearing through FRFR is a mic'd representation of the cabs. It takes some getting used to. You have to start thinking like a producer/engineer rather than a guitar player. If you start trying to dial out what you call "fizz" and "artifacts" you're going to end up with a tone that doesn't cut. It might sound good to you but it won't fit in the mix. That fizz and sizzle is what makes those classic rock tones work. Listen to some isolated tracks of VH and AC/DC and you'll hear a ton of high-end sizzle. In the mix, however, it's not noticeable. If you remove it then the guitar sounds dead.
[113] The sound of an amp in the "far field" is quite different than what you get with close-miking. IR's are made using close-miking and therefore sound nothing like listening to a guitar cab at distance from the cone.
Your audience does not hear the far field tone, they hear the close-miked tone as that's what is put through the FOH.
It can be quite an adjustment coming from far field amp tone to close-miked tone. Some people just never adjust.
Fortunately the Axe-Fx was designed to give you the best of both worlds. You can use the FX Loop and Output 2 to a power amp and conventional guitar cab while routing the fully processed tone with IR to the FOH. See the manual for full details. Rather than using your amp you can use a lightweight solid-state power amp and any of the new, lightweight guitar cabs that use Neodymium speakers. This gives you the classic far field amp tone for yourself in a lightweight package and the polished sound for the FOH direct from Output 1.
[114] Apples-to-oranges. You FRFR setup is using close-mic'd IRs. They typically have a lot more high frequencies than what you hear at a distance and off-axis from the speaker.
[115] […] All speakers "move air", that's the entire point of their design. Guitar speakers are inherently directional at higher frequencies. So when you stand off to the side you hear less highs. If you have two or four speakers the directivity gets even worse. FRFR speakers have less directivity. This combined with IR technology that almost invariably uses samples of a close-miked speaker and you end up with a different listening experience. To confuse the issue further many combo amps have an open back which changes the frequency response at the listening position even more.
Now, if you connect your Axe-Fx to a power amp and traditional 1x12, 2x12, etc. then you will get "amp in the room" but the "moving air" statement has no basis in fact.
[116] […] You can't compare what you are used to hearing "in the room". The close-miked sound ALWAYS has more highs and lows. This is due to the physics of near-field micing. And this is why a highpass and lowpass are frequently employed at mixdown.
[117] […] The classic method is "1W / 1m" which is to apply 1W and measure 1 meter away. When you get the microphone close to the speaker the response is much different and you usually get more highs and lows. This is "close miked" and is the technique normally used in studio recordings. During mixdown the producer/engineer will then often highpass and lowpass the signal to remove these excess highs and lows and to make the guitar "sit in the mix".
IRs are almost always made using the same close-miked technique and, hence, will sound like a raw recording. Far-field IRs are possible but very difficult to obtain requiring a large facility and special techniques.
Our primary goal is to model an amplifier and speaker as accurately as possible and the latest modeling is astonishingly accurate. We do not purport to be producers or mix engineers and leave the choice of low cut and high cut frequencies up to the user. Furthermore many users rely on the soundman to apply the filtering at the board, just as they would when mic'ing a "real" amp. More importantly the choice of frequencies is highly dependent upon the IR used.
[118] IRs are equivalent to close-mic'ing an amp. When you close mic an amp you almost always get more bass and treble than an "amp in the room". The extra bass is due to the proximity effect of the microphone. The extra treble is primarily due to the directivity of the speaker.
During mixdown engineers/producers will typically incorporate a low cut and high cut to help the sound "sit in the mix".
The thing to take away from all this is that an IR represents the close mic'd sound (unless using far-field IRs which are rare) and the close mic'd sound of an amp is much different than the "amp in the room" sound. As such it is common to use frequency shaping on a close-mic'd amp.
[119] The Axe-Fx is extremely accurate in duplicating the sound of a mic'd amp. Your monitoring thus becomes an essential part of the chain and accuracy is paramount. Many "FRFR" monitors are neither FR nor FR.
[120] FRFR is just not the same. Traditional head/cab you hear the sound from a bandwidth-restricted speaker at, say, 10 ft. In a typical modeler setup you are hearing what the "mic heard" when the IR was made and that mic was pushed up against the grill cloth. One approach is to use "far field" IRs which are obtained using a measurement mic at a typical listening distance and angle. These are rare. There are a couple stock far-field IRs. They are indicated by (JM) for Jay Mitchell, who created them. Even then it's still not the same because when you are using a traditional setup you move around while playing and the tone changes based on the angle. With a far-field IR the tone doesn't change with angle. When I was gigging I used a power amp and cab behind me and sent the XLR outputs to FOH. More gear to lug but best of both worlds: traditional backline sound, consistent FOH sound.
[121] It's not the mic per se'. It's near-field vs. far field. Different mics sample the near-field differently. Mic'ing a speaker is sampling the near-field which sounds dramatically different than the far field. The response pattern of the mic samples the near-field and mics each have their unique pattern. Regardless, it's irrelevant. You'll never get monitors to sound like "cab in the room". If you want that use a SS power amp and cab.
FRFR is simply different. It's like mic'ing up the cab in an iso booth and listening from the control room. Therefore it becomes EXTREMELY dependent upon the FRFR speaker. (...) if you have access to some nice studio monitors I'd start there.
Apples and oranges. You're comparing FRFR to amp-in-the-room. They will never sound the same. And, IMO, those Matrix FRFR cabs sound like garbage but that's another story. When you use cabinet modeling into an FRFR you're recreating the sound of a close-mic'd amp. It's analogous to being in the control room while listening to your cab in an isolation booth. I.e., how records are made. If you want to compare to a head plugged into a cab you need to run the Axe-Fx into a power amp into the same cab. Get a *good" solid-state or tube power amp and run that into a Marshall cab. A few tweaks and it should sound nearly identical.
[122] Far-field IRs are not the panacea some are making them out to be. Some things need clarification:
- A far-field IR will still not sound exactly like "amp in the room". The reason for this is that the dispersion of a guitar cabinet is very different than that of a FRFR speaker. An FRFR speaker has far wider dispersion at high frequencies, by design. With a guitar cabinet the low frequencies are less directional than the highs. This causes the cab to interact with the room differently. So even if you capture a far-field IR it will not sound the same through a FRFR speaker.
- Most of the time we are not in the far-field of a guitar cabinet. At 10 kHz the far-field of a 12" speaker is about 18 ft. So usually we're in the far-field at some frequencies but in the Fresnel zone at others. At a typical distance of, say, 5 ft. we are only in the far-field at frequencies below roughly 3 kHz. Above that we are in the Fresnel zone.
- Because of #2 the sound at each ear can be quite a bit different. That six inches or so between our ears makes a big difference. When using a far-field IR the same sound will be presented to each ear. Even when in the far-field the sound changes pretty dramatically vs. angle because the dispersion is a function of frequency. One ear will hear more highs than the other.
- A cab with more than one speaker creates significant challenges. For example, a 4x12 has a far-field at 10 kHz that's roughly 100 feet! If you capture an IR of that cab at, say, 10 feet you are nowhere near the far-field. At anything other than nadir (aka boresight, 0 degrees) the individual speakers will contribute with different times of arrival. This results in extremely phasey sound (we were able to get some 4x12 IRs by using a special trick but in general you need to be very far away).
- We don't hear this phasiness when listening to the real cab though because of #2. We get very different signals at each ear and our brain processes these. When using a Fresnel-zone IR of a 4x12 the same signal goes to both ears.
- Many guitar cabs are open back. A far-field IR of an open back cab through an FRFR monitor will sound very different because you're not reproducing the sound coming out of the back of the cab and bouncing off the walls.
- The sound of recorded guitar is near-field. This is what most people are used to hearing. So if you're trying to get the sound of your favorite record you won't get that with far-field IRs.
The takeaway from all this is that if you truly want the sound of amp in the room the best way to get that is to use an actual guitar cab. This isn't to say that far-field IRs are useless. They will give you a roughly similar sound to a guitar cab but it's just not the same.
[123] You'll never get the same experience using FRFR compared to AITR. It's physics. It's not a bunch of internet myth and pseudo-science about "mojo" and "tube magic.
Fletcher-Munson
The Fletcher-Munson curve
, or Equal-loudness contour
is the scientific name for the fact that human ears perceive sound at low volume levels differently than at higher levels. This is VERY important when dialing in tones.
When tweaking tone at low volume levels, a player often turns up treble and bass. This is what the Loudness
switch on older home stereo systems did.
When the volume is turned up, those high and low frequencies get harsh and boomy. That guitar sound then competes with cymbals, and will lose. Also, the guitar competes with the bass guitar, and will lose.
This is not specific to FRFR systems, but FRFR amplification makes the Fletcher-Munson effect much more apparent because it amplifies a broad frequency range. In comparison, a traditional guitar speaker operates as a filter, with quite a narrow frequency range.
FRACTAL AUDIO QUOTES
The "Loudness" controls in old Hi-Fi gear was nothing more than a bass/treble boost. It's a gimmick. It was supposed to compensate for the reduced sensitivity of human hearing at lower volumes. It's not accurate, never was and can never be. There are a myriad of reasons why, the most glaring is that you have no way of knowing what the SPL is (without a meter). Since equal loudness contours are dependent on SPL you can't compensate if you don't know the SPL. The Axe-Fx has no idea of the sensitivity of the amplifier and speakers connected. Therefore it can't possibly know what the SPL is and concomitantly can't know how to compensate.
[124] People dial in modelers at low volumes and (usually unwittingly) compensate for F-M. Then when they turn up at a gig the lows are boomy and the highs are piercing. Tube amps are voiced for gig volumes. Therefore it is logical to dial in your presets at gig volume.
For more information about Fletcher-Munson curves or Equal-loudness see:
Equal-loudness contour
at Wikipedia.The Fletcher Munson Curve & Why You Should Know About It
at ZeSoundSuite Dot Com.Crafting Loud Mixes That Sound Great
at Sound on Sound.The Fletcher Munson Curve explained
at E-Home Recording Studio.
Fighting extended frequencies and Fletcher-Munson
Above, we concluded that the FRFR sound has an extended frequency range, which is often undesirable for a guitar sound and can suffer from the Fletcher-Munson curve when not dialed in correctly.
The solution to these issues is really simple: Don't dial in too much top and bottom end, and always dial in your live guitar tones at gig levels, 90dB and higher. Do NOT expect excellent bedroom
or headphone tones to translate well to a rehearsal room or stage because our perception of sound changes as the volume changes. What sounds dull at low volume, may sound fantastic at high volume. And remember that the guitar is a mid
instrument, so focus on the midrange.
So, how do you tweak the sound for FRFR? Here are some guidelines and options:
- Use the Low Cut and High Cut parameters in the Cab block to block undesirable top and bottom end. Common values are cutting lows, using
high-pass
between 120-150Hz and cutting highs, orlow-pass
, between 5-10kHz. This may seem to make your guitar sound bad or dull by itself, but it will improve its sound within the entire mix. - Put a PEQ or GEQ block at the end of the grid and block the lower and higher frequencies.
- Adjust Depth/Bass and Treble/Presence in the Amp block.
- Boost the mids. For example: Put a PEQ at the end of the grid, set a band, using Peaking when using the first or last band, to 770 hz, Q at 0.35, Gain between 2 and 4 dB. Or, bump the middle slider of a 5-band Passive GEQ.
- Use the Cut switch in the Amp block.
- Add the Factory
1 - 1x4 Pig 57
IR to add body to the sound.
FRACTAL AUDIO QUOTES
[125] Resist the temptation to add bass and treble. The amp designers knew what they were doing (well most of them). If you are applying heavy EQ then you will be disappointed at gig volumes. What sounds midrangey and bland at low volumes will sound great at high volumes.
Do some research on Fletcher-Munson to understand this.
[126] People often talk about applying low cuts and high cuts. This is because the cabinet models used in modelers are almost always (with a couple exceptions) based on near-field samples of guitar cabinets. IOW, the mic is pushed up against the grill cloth. This just happens to be the way that record producers/engineers mic a cabinet in the studio and the way guitar cabs are mic'd on stage. This is done primarily for isolation reasons.
The downside of this approach is that the resulting tone will have a lot more lows and highs than when listening to the amp+cab "in the room". What the mic "hears" when pushed up against the grill cloth is not the same thing that we hear standing 10 feet away.
The most common technique to deal with this is to simply cut out the lows and highs using blocking filters, e.g. highpass and lowpass filters. Producers routinely do this when mixing as excessive amounts of lows and highs will cause the guitar tracks to get "lost in the mix". Live sound engineers often do the same thing.
The Cabinet block has blocking filters built in for just this very reason. You can also use a couple dedicated filter blocks or a parametric EQ block. For now let's use the Cabinet block. My personal settings are Low Cut around 80 Hz and High Cut around 7500 Hz and Filter Slope set to 12 dB/octave but these are just a starting point.
Far-field IRs are available but they are rare due to the difficulty in obtaining them. They require a large facility and special techniques making the process impractical in most cases. So, until an abundant source of far-field IRs are available we need to think like a producer/engineer who is dealing with the mic pushed up against the grill cloth. This means shaping the tone with EQ to remove unwanted frequencies.
Optimize the Amp block's Output Mode
The Axe-Fx III, FM3 and FM9 let you optimize the Amp block's output for the chosen amplification method. Options are:
FRFR — when using low-to-medium volume FRFR amplification
SS PA + Cab — when using a solid-state power amplifier and a traditional guitar speaker
FRACTAL AUDIO QUOTES
[127] Added Output Mode to Amp block. The default value, FRFR, is the classic mode and designed for use with monitors or recording. The SS PA + Cab mode is intended for use with a solid-state power amp and conventional guitar cab. In this mode speaker compression modeling behaves differently relying on the speaker for compression while still simulating the interaction with the power amp. NOTE: this mode is not intended for use with current drive power amps, i.e. tube power amps, Class-D current feedback amps (Quilter Tone Block), etc. NOTE: this mode CAN be used with FRFR monitors in high volume applications where the monitor’s speakers are compressing thereby achieving a more dynamic response.
[128] The default output mode assumes the speaker is a monitor-type speaker. It models the compression of the guitar speaker and transient response and assumes the reproduction speaker is "ideal". SS PWR AMP + CAB mode turns off the speaker modeling aspect because you're using a real guitar speaker.
Stick to the
FRFRsetting when simultaneously using FRFR monitoring/direct-to-FOH and a solid-state power amp and conventional guitar cab on stage.
Recommended Amp and Cab settings
For more information see Table: amp settings, depending on power amp and speaker
for the recommended Amp and Cab settings for each type of amplification.
FRFR and amp/cab-in-the-room
Use the parameters below to get the sound of FRFR amplification closer to the familiar amp/cab in the room
sound.
Cab block:
- use Room Level.
- use Floor Reflections.
- use FullRes IRs to add room ambience.
- select a
far-field
IR. The stock ones haveJM
in their name. Or, select a stock cab which has been captured with a neutral mic, such as the Red Wirez ones, and set Proximity to its lowest value for simulate far-field coloring. - create the so-called
HAAS
effect by using two IRs in stereo, with a very short delay in the Cab block on one of them. - use Smoothing.
- use Low Cut and High Cut to shave off excessive low and high frequencies and mimic the frequency range of a traditional guitar speaker.
- add the Factory 1 - 1x4 Pig 57 IR to add body to the sound.
- bump the middle slider of a 5-band Passive GEQ.
Amp block: Use:
- Speaker Compression
- Speaker Compliance
- Speaker Drive
- Speaker Thump
Or, use a Filter instead of a Cab block. See the following for more information:
- YouTube: Fractal Friday with Cooper Carter #19
Instant Fractal
.Amp in the Room
Tone - Cliff's walk-through in
Amp in the Room?
in the forum.
In the end, if you crave a real amp/cab in the room
tone from your modeler, just amplify it through a power amp and a traditional guitar speaker cabinet.
FRACTAL AUDIO QUOTES
[129] You'll never get monitors to sound like "cab in the room". If you want that use a SS power amp and cab. No amount of forum discussion is going to change physics.
Do not put a microphone in front of a FRFR speaker
When you're using FRFR amplification on stage and you need to provide a signal for FOH, do NOT place a microphone in front of the FRFR monitor. That would make no sense: the source signal already contains the sound of a close-miked guitar cab. Direct-to-FOH is the right way to do it: run a cable from the output(s) to the mixing console. For long distances, use the balanced outputs.
Tweeter squeal from FRFR speakers
Some FRFR speakers can emit very high-pitched loud feedback.
FRACTAL AUDIO QUOTES
[130] Tweeter squeal is magnetic feedback from the speaker's tweeter. Move further away from the speakers. This is a phenomenon unique to FRFR solutions.
[131] Magnetic feedback is an issue unique to FRFR amplification. The tweeter creates a magnetic feedback loop with the pickups. The closer you get to the speaker the more feedback until the point it squeals. The only solution is to move away from the speaker or turn down the gain/volume.
[132] The high-pitched feedback is pickup squeal and is caused by electromagnetic feedback from the speaker to your pickups. FRFR tends to exacerbate this since you have a tweeter feeding back high frequencies. A noise gate can help but the best solution is to move away from the speaker.
[133] If the tweeter is not magnetically shielded the magnetic field will couple into the guitar's pickups causing a feedback loop. The issue is exacerbated by high gain. The solution is to use a monitor expressly designed for use with a modeler like the Atomic CLR, Line 6 Powercab, etc. Another solution is to monitor yourself using a conventional guitar cabinet and dedicated power amp.
[134] This is magnetic feedback not acoustic feedback. At high volumes the magnetic field from the tweeter(s) couples into the pickups enough to cause a feedback loop. The solution is to move away from the speakers.
Power amp and guitar speaker
See the rig diagrams in Section 4 of the Axe-Fx III Owner's Manual.
Why use a power amp and guitar speaker
If you need amplification, and Full Range Flat Response is not your thing
, you can amplify the amp modeler using a power amp and a guitar speaker.
When choosing this route, there are still choices to be made, as explained in the sections below.
FRACTAL AUDIO QUOTES
[135] You'll never get monitors to sound like "cab in the room". If you want that use a SS power amp and cab. No amount of forum discussion is going to change physics.
Using a tube power amp for guitar or head or combo
When using the amp modeler with a tube-powered amp which is designed for guitars, like Mesa, VHT, Fryette, and a traditional speaker cabinet:
- Switch off Power Amp Modeling.
- Disable Cabinet Modeling, because you're using a traditional guitar speaker.
- Set the controls on the power amp as neutral as possible.
This also applies when connecting the amp modeler to the Effects Return port of a guitar combo amp or an amp head.
FRACTAL AUDIO QUOTES
[136] If you use a tube power amp and don't turn off power amp modeling in the Axe-Fx you will get the impression that the tube power amp sounds "bigger" and "warmer". This is because the tube power amp will have more bass (and highs) than the solid-state power amp since a tube power amp's response follows the speaker impedance.
People will ALWAYS find that more bass and treble sounds "better" when listening alone but in a band context that tone will get lost. Speaker designers have been exploiting this fact of human perception for decades. Many "hi-fi" speakers exaggerate the bass and treble because the uneducated customer will think they sound "better". A truly flat speaker will sound dull in comparison to one with exaggerated lows and highs. Over time, however, those exaggerated frequencies lead to fatigue. It's only in comparison that exaggerated bass and treble sound "better". In an isolated context this aspect of human perception is not evident.
[137] If you are using a "tube" power amp you should set any Presence, Depth, Resonance, etc. controls to their minimum positions on that amp (assuming they are conventional controls).
[…] Set them to noon on Mesa stuff.
[…] The Presence control on Mesa amps is most neutral around noon. If you turn it up it boosts the highs, if you turn it down it cuts the highs. On most other power amps it only boosts.
[138] If using a tube power amp into a traditional cab all should be zero. If using a solid-state amp into a traditional cab I would recommend Speaker Compression and Compliance not be zero.
Neutral tube power amp
When using the amp modeler with a neutral
tube power amp, like Fryette's Power Station, and a traditional speaker cabinet:
- Keep Power Amp Modeling turned on.
- Disable Cabinet Modeling, because you're using a traditional guitar speaker.
- Set Speaker Impedance Curve to
Resistive Load
. Note: if you use the same Amp block for a separate direct signal (to FOH or FRFR monitor), the direct tone will be effected.
FRACTAL AUDIO QUOTES
[139] If using a tube power amp into a traditional cab all should be zero. If using a solid-state amp into a traditional cab I would recommend Speaker Compression and Compliance not be zero.
For more information see Fryette LXII power amp
at TGP.
Solid-state power amp
When using the amp modeler with a solid-state power amp, no tubes, like a Matrix, Seymour Duncan, or Crown, and a traditional speaker cabinet:
- Keep Power Amp Modeling turned on.
- Disable Cabinet Modeling, because you're using a traditional guitar speaker.
- Turn down Speaker Drive in the Amp block. Turning down Speaker Compression, Speaker Compliance and Cabinet Resonance is not required. .
- Set the Amp block's Output Mode to: SS Amp + Cab.
FRACTAL AUDIO QUOTES
[140] If using a tube power amp into a traditional cab all should be zero. If using a solid-state amp into a traditional cab I would recommend Speaker Compression and Compliance not be zero.
[141] Added Output Mode to Amp block. The default value, FRFR, is the classic mode and designed for use with monitors or recording. The SS PA + Cab mode is intended for use with a solid-state power amp and conventional guitar cab. In this mode speaker compression modeling behaves differently relying on the speaker for compression while still simulating the interaction with the power amp. NOTE: this mode is not intended for use with current drive power amps, i.e. tube power amps, Class-D current feedback amps (Quilter Tone Block), etc. NOTE: this mode CAN be used with FRFR monitors in high volume applications where the monitor’s speakers are compressing thereby achieving a more dynamic response.
[142] A lot of it is about transient energy storage. A tube amp stores a LOT of energy. Take a typical 100W tube amp like a Diezel. It will typically have 220uF of reservoir capacitance and a B+ of 450V. The energy stored is 22.3 Joules!!!
Now take a typical consumer Class-D "500W" power amp (actual continuous power about 100W). They usually have voltage rails around 50V and 680uF or so of capacitance. The energy stored (assuming bipolar supplies) is 1.7 Joules.
The tube amp has over 13 times the energy storage. So those palm mute transients are reproduced accurately. The Class-D amp runs out of gas.
For example, if your transient duration is, say, 100ms, and you're pushing a full 100W then the energy required is 10 Joules. The Class-D amp simply can't do it.
It's one of my pet peeves. People use cheap, low-end, consumer grade Class-D power amps and then make bold proclamations that the models don't sound as good as the real amp without understanding even a lick of the physics involved.
[143] MAKE SURE YOU SET THE OUTPUT MODE OF THE AMP BLOCK TO "SS PWR AMP + CAB".
The default output mode assumes the speaker is a monitor-type speaker. It models the compression of the guitar speaker and transient response and assumes the reproduction speaker is "ideal".
SS PWR AMP + CAB mode turns off the speaker modeling aspect because you're using a real guitar speaker.
[144] Turn Speaker Drive and Thump off to start. You may want to turn them up if you're listening at lower volumes.
[145] Ignoring the effects of speaker displacement on speaker impedance the *voltage* out of a tube power amp is proportional to the speaker impedance. The speaker impedance is a function of frequency. This boosts the lows and highs.
The voltage clips at the power rails so the lows and highs clip before the midrange. Therefore when you push a tube power amp into clipping the mids get emphasized.
Negative feedback reduces the output impedance and therefore makes the voltage less dependent upon the impedance.
Most of these tube preamp things with integrated "power amp simulation" and IR loaders use a simple static EQ to model the power amp. The TMP also uses static EQ to model impedance dependency but "bakes it" into the IR (for some weird reason).
In a real speaker the impedance is dependent upon the speaker displacement. The voice coil inductance decreases as the coil leaves the gap. This makes sense because there's less magnet inside the coil and inductance is dependent upon the magnetic field. The low frequency resonance also changes with displacement via a more complex relationship. FWIW, our products model this stuff.
The moral of the story is that, yes, you can simulate a tube power amp (crudely) with a static EQ. It won't simulate the clipping but if it's a high-gain tone where the preamp is doing the distortion then it's probably good enough for that genre.
IMO "good" tube tone is a combination of preamp and power amp distortion. Relying on preamp distortion can make things sound a bit flat as preamp distortion lacks dynamics. Power amp distortion alone can be a bit flubby. If you balance the two you get a more dynamic experience with more "character".
[146] A speaker responds to the voltage on its terminals. If you model everything accurately and then simply amplify that signal and send it to a speaker the results will be the same. The hard parts are modeling it accurately and amplifying it correctly.
Modeling it accurately means modeling the speaker impedance which is often not known and accurately modeling the I-V relationship of the power tubes. The latter is extremely difficult and requires a lot of processing power. Inexpensive products use waveshaping and EQ approaches. We use nonlinear ODEs and iterative solvers.
Amplifying it correctly means an amplifier with significant power reserves. Most of these small, cheap Class-D amps simply don't have the power reserves to replicate a cranked 100W tube amp. The transient response is lost because the amplifier runs out of energy. They aren't designed for these sorts of applications. They're meant for low-cost consumer applications.
High-end solid-state amps, whether Class-AB, Class-D, Class-G, etc. (i.e. Crown, QSC, etc.) have the requisite energy reserves and I bet anyone would be hard-pressed to tell the difference in an A/B test (assuming the speaker impedance were set correctly).
I've done tests comparing various 100W amps using a Crown K2 and, a Matrix (something, forget the actual model but it was 1000W+) . The differences were negligible IMO. In fact, I could tweak the speaker impedance curve and end up with something that actually sounded better.
It really depends on your application. At loud stage volumes an inexpensive Class-D power amp isn't the right tool for the job. In a small club application then it's probably fine. Don't confuse misapplication with some nebulous physical shortcoming of the various technologies.
Finding the resonant frequency with a solid-state amplifier
A solid-state amp doesn't automatically interact with the speaker like a tube amp does, which is why the Amp block provides impedance and resonance parameters. The default Low Frequency Resonance value may not get the best results with the speaker in use. Optimize this by finding the resonant frequency of the cabinet, like this:
- Put a Filter block after the Amp block.
- Set the type to Peaking, Q to 5 or so and Gain to 10 dB.
- Start with a Frequency of around 50 Hz. Play some chugga-chugga and slowly adjust the Frequency until you hear and feel the cabinet resonate. You need to do this at loud volume level to notice it. Make a note of the frequency.
- Remove the Filter block and set the Amp block's Low Frequency Resonance value to match.
Alternatively:
- Add a Synth block (after the Amp block) to the preset and make sure it is connected to the grid output.
- Select Sine wave.
- Turn off Tracking.
- Turn up the volume of your rig.
- Adjust Frequency until you hear and feel the cabinet resonate. You need to do this at loud volume level to notice it. Make a note of the frequency.
- Remove the Synth block and set the Amp block's Low Frequency Resonance value to match.
FRACTAL AUDIO QUOTES
[147] I often do A/B tests with a real amp into a cab and an Axe-Fx into a Matrix into the same cab. The cab is a stereo 2x12, once side is the real amp the other is the Axe-Fx. Once I adjust the impedance curve there is no difference in "movement" between the two and, if anything, the Axe-Fx often sounds better because it has less noise and hum.
Gain-staging a power amp
Make sure not to overload the input of a connected power amp or active monitor.
FRACTAL AUDIO QUOTES
[148] The II actually has more output than the I. The II can do about +20 dBu, the I was about +18.
[149] Start with amp volume at noon. Bring up Axe-Fx volume until desired level is reached. If you need more, turn up amp. With the Axe-Fx volume all the way up you would be pushing +20 dBu into the amp which could clip the inputs to the amp.
Note: it's common knowledge that a Matrix power amplifier (GT800FX, GT1000FX) sounds at its best with level at 2 o'clock or higher.
About speaker wire/speaker cable
FRACTAL AUDIO QUOTES
[150] The Axe-Fx is designed to recreate the signal at the speaker jack of a tube amp and it does this tremendously well. If I do a Tone Match to the output of the amp vs. the model it's almost always nearly a perfectly flat line.
So today I was playing around and did a quick tone match to one of my Plexis and then a Suhr Badger and the results showed a significant mid-scoop (2-3 dB). I was puzzled. Had I messed something up in the new firmware? I repeated the tone match using a DI off the speaker jack and the result was a perfectly flat line. Then I realized that the difference was due to this 30 ft speaker cable I was using because the speaker cab was remote from the amp. Just a bit surprised that that little resistance could have that much effect.
Fortunately the new Cab-Lab addresses all this by allowing you to capture reference IRs and we've included reference IRs along with our latest Cab-Pack.
To double-check I then captured a reference IR off the speaker and corrected the IR using the new Cab-Lab and viola, perfectly flat.
[151] There's a big difference between a long cable between your guitar and amp and a long speaker cord. A long instrument cord loads your guitar's pickups with a reactive load that's mostly capacitive. This changes the resonant frequency of the pickups and rolls off the highs. A long speaker cord increases the resistance between the amp and the speaker which decreases the damping factor. A lower damping factor means the response follows the impedance curve of the speaker more than a high damping factor.
[152] For 5m regular ol' 14-16 gauge speaker cable is fine.
Recommended Amp and Cab settings
See Table: amp settings, depending on power amp and speaker
for each type of amplification.
Combine FRFR with a traditional backline rig
Fractal Audio's amp modelers allow a combination of different output/amplification methods. Many players amplify their modeler on stage in the traditional backline
way by using a speaker cabinet with a power amp, with a direct signal going from the modeler to the PA system. The modelers have a factory preset designed for this purpose.
Choose between these methods:
Axe-Fx III, FM9 and FM3
- Use multiple Output blocks and signal chains to handle multiple outgoing signals.
- See the rig diagrams in Section 4 of the Owner's Manual.
Axe-Fx II and AX8
- Insert an FXL block and make it part of the routing but don't connect it to the grid output. The signal before the FXL block will be sent to Output 2. This method is more flexible than the one above, because the position of the FXL block determines which part of the signal is being sent to Output 2. For example, placing FXL before or after a Cabinet block determines whether the Output 2 signal includes cabinet modeling or not. Use this when you want your FOH signal to be "direct" (including cab modeling) and your stage sound to come from a traditional cabinet (without cab modeling). Among the factory presets is a template. The Axe-Fx II lets you put FXL in series or parallel, but the AX8 requires FXL in a parallel row to prevent a feedback loop.
Playing the Axe-Fx II Direct to FOH & with Onstage Cabs
is a video tutorial with more information. - Split the signal at the end of the grid into a row with a Cab block and a row with a shunt. In the Output Mixer pan those rows 100% left (Cab) and right (shunt). Now OUT1 Left is the signal with cabinet modeling, and OUT1 Right is the signal without cabinet modeling. This method allows you to use the stereo effects loop for other purposes. [153]
PREVIOUS GENERATIONS
Axe-Fx II and AX8:
[154] Fortunately the Axe-Fx was designed to give you the best of both worlds. You can use the FX Loop and Output 2 to a power amp and conventional guitar cab while routing the fully processed tone with IR to the FOH. See the manual for full details. Rather than using your amp you can use a lightweight solid-state power amp and any of the new, lightweight guitar cabs that use Neodymium speakers. This gives you the classic far field amp tone for yourself in a lightweight package and the polished sound for the FOH direct from Output 1.
[155] When I was gigging I used a power amp and cab behind me and sent the XLR outputs to FOH. More gear to lug but best of both worlds: traditional backline sound, consistent FOH sound.
Table: amp settings, depending on power amp and speaker
has recommended Amp and Cab settings for each type of amplification.
4CM (Four Cable Method)
The Four Cable Method
, or 4CM
, is the common term for a rig that lets you run effects before the amp AND after the effects loop.
See the rig diagrams in Section 4 of the Owner's Manual.
Axe-Fx III – Use I/O 3 or I/O 4
FM9 — Use I/O 3
FM3 — Use I/O 2
In all of the above cases, turn the front panel output knob fully open for unity gain, adjust Boost/Pad in the I/O menu for optimal SNR, and adjust levels where needed.
VP4 – The VP4 has a dedicated 4CM configuration mode in SETUP and must be used with dedicated 4CM presets. Read the section in its Owners manual and its 4CM guide, and read this: 4CM.
Axe-Fx II – Adjust Boost/Pad and Input Level in the I/O menu to optimize the signal. Also, turn the Output Level knob fully open for unity gain. You can't combine 4CM with cab modeling.
AX8 – The AX8 is not optimized for 4CM, but it will work. The process is the same as the Axe-Fx II.
FX8 – See FX8 below.
FRACTAL AUDIO QUOTES
Axe-Fx III:
[156] The Axe-Fx III excels in 4CM. Outputs 3 and 4 are specifically designed to support this (unity gain mode support).
[157] The analog signal path in the Axe-Fx III is the same as the FX8.
[158] The only product more transparent than the FX-8 is the Axe-Fx III.
FM9:
[159] 4CM should work great. The FM9 uses the same "flagship" analog processing as the Axe-Fx III which evolved from the FX8. The FX8 was the best analog path I'd ever designed but the product, unfortunately, did not sell well. I took that design, tweaked it a bit and used it in the Axe-Fx III.
FM3:
[160] The FM3 isn't expressly designed with 4CM in mind like the Axe-Fx III. It can do it but it's not as easy and may not have the same level of fidelity.
Axe-FX II:
[161] The very early Axe-Fx II's had more bandwidth than necessary on Output 2. The frequency response extended to hundreds of kHz. When used with certain tube amps this would cause instability in the output drivers. The solution was to limit the bandwidth to a "normal" range of 20 to 20 kHz. We provided the update for free and all units shipped after the first 100 or so had this update included. The Axe-Fx II Mark II, XL and XL+ have a redesigned output circuit that is immune from any of these issues.
Axe-FX XL and XL+:
[162] It is very difficult to minimize the hiss when putting a digital processor in front of a high-gain amp due to the A/D and D/A conversions. The XL is probably one of the quietest processors made but there will still be some residual hiss when using high gain. The Output 2 Boost/Pad feature was specifically intended to minimize hiss in these scenarios by running the D/A converter as "hot" as possible and then reducing the signal level after the converter with an analog pad.
[163] The XL+ shares the same amazing low-noise architecture of the FX8. I regularly use my XL+ in 4CM as this is part of the modeling process. It's the quietest device I've ever tried in 4CM.
Leon Todd's video FM3 + Tube Amp - 4CM Tutorial
has more information as does Ola Englund's video LIVE RIG 2016 - Satan, AX8, 4 cable method
.
Effects only (Pre and Post)
PRE effects
- Use Output 2 on the Axe-Fx II, FM3 and AX8, and Input/Output 3 or 4 on the Axe-Fx III and FM9.
- In I/O set output level to -10 dB if possible.
- Adjust Boost/Pad to make sure the full range of the D/A converter is used and turn up the Output knob all the way for unity gain.
- Test the setup by creating a preset with shunts only. The level should be the same as when leaving out the processor. Then start adding effect blocks without the Amp or Cab blocks.
Axe-Fx III, FM3 and FM9: see the rig diagram in Section 4 of the Owner's Manual.
VP4: read the Owners manual. Sets of factory presets are configured specifically for Pre operation. A list of VP4 factory presets is included at the the end of its Owners manual.
POST effects
When using the Axe-Fx II or III, AX8, FM9 or FM3 as an effects-only device in an amp's effects loop, you probably want it to send and receive line level signals, at unity gain.
- Use Input 2 and Output 2 on the Axe-Fx II, FM3 and AX8, and Input/Output 3 on the FM9, or Input/Output 3 or 4 on the Axe-Fx III.
- Adjust Input Level for an optimal signal-to-noise ratio.
- Select the correct input and output settings in I/O.
- Set the Output 2 knob to its maximum position to enable unity gain.
- Test the setup by creating a preset with shunts only. The level should be the same as when leaving out the processor. Then start adding effect blocks (no Amp or Cab).
On the Axe-Fx III and FM9, see the rig diagram in Section 4 of the Owner's Manual.
Some amps require inserting a dummy jack into the effects loop's Send to activate the effects loop.
VP4: read the Owners manual. Sets of factory presets are configured specifically for Post operation. A list of VP4 factory presets is included at the the end of its Owners manual.
FRACTAL AUDIO QUOTES
[164] You should NOT use Boost/Pad in this configuration.
[165] If you are going into the front of an amp and using the FM3 for effects only then use Output 2 and increase the Boost/Pad in SETUP. This will optimize the SNR.
Digital I/O and audio
See Digital I/O and audio
for information.
IR loader
The Axe-Fx III, FM3, FM9 and AX8 can be used as an IR loader.
- Connect the guitar to an amp head.
- Connect the amp's speaker output to a load box, such as Fractal Audio's X-Load.
- Connect the loadbox to the AX8, FM3, FM9 or Axe-Fx.
- Use a preset with a Cab block (or the IR Player block on the Axe-Fx III), and without an Amp block.
See the following videos for demonstrations:
- Leon Todd's
AX8 Basics - 3CM
- Nicolas Rivera's
Suhr Badger 18 vs Fractal Badger 18 Emulation
Surround or quadraphonic sound
Use one stereo output for two front monitors. Use another for two rear monitors. Split the signal on the grid, and send it through 100% wet Reverb to the output feeding the rear monitors. Verify that both outputs are turned up on the front panel.
Yek's tutorial Have 4 monitors? Use two stereo outputs to achieve semi-surround sound
has more information.
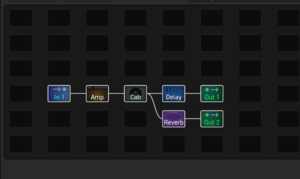
FX8
As a pedalboard (PRE effects)
- Guitar goes into IN [PRE] / INSTR. Note: this input only feeds effect blocks designated as PRE.
- OUT [PRE] LEFT goes into the amplifier's guitar input. Use a Humbuster cable to prevent noise.
- You can use default FX8 settings. Exception: change the output mode in I/O > Audio (see manual for stereo operation)to Mono (see manual for stereo operation).
You can also use this setup to connect an FX8 to the Axe-Fx.
More information is available in the Owner's Manual, including a description of the cables required.
In an amplifier's effects loop (POST effects)
- Guitar goes straight into the amplifier.
- Amp's effects loop SEND goes into IN [POST] LEFT.
- Amp's effects loop RETURN goes into OUT [POST] LEFT. Use a Humbuster cable to prevent noise.
- You can use default FX8 settings. Exceptions:
- Change the output mode in I/O > Audio to Mono (see manual for stereo operation).
- Change Global Looper Location to OUT POST.
- Change Global Detector to IN [POST].
Four Cable Method (4CM)
The FX8 can be set up to put effects before the amp as well as in the amp's effects loop.
- Guitar goes into IN [PRE] / INSTR.
- OUT [PRE] LEFT goes into the amp's guitar's input. Use a Humbuster cable to prevent noise.
- The amp's effects loop SEND goes into IN [POST] LEFT.
- The amp's effects loop RETURN goes into OUT [POST] LEFT. Use a Humbuster cable to prevent noise.
- You can use default FX8 settings. Exceptions:
- Change the output mode in I/O > Audio to Mono (see manual for stereo operation).
- Change Global Looper Location to OUT POST.
Note: In the two scenarios above, the outputs are buffered for long cable runs.
If you have the FX8 set up for 4CM and want to change this, for example to put the FX8 before a computer, just use a jumper cable to connect OUT PRE L MONO to IN POST L, with OUT POST L going to the computer, amp or whatever. All effects will work and there's no need to change stuff in the configuration.
If you're using the FX8 in a 4CM setup and you're experiencing hiss, try another Post Level value.
Combine FX8 with Axe-Fx or AX8
You can use the FX8 for "pre" effects where you plug the guitar into the FX8, Axe-Fx or AX8 for post-effects, including amp and cabinet modeling where you plug the FX8 into the Axe-Fx or AX8. By adding a MIDI connection you can change Axe-Fx and AX8 presets from the FX8.
Relays: switch amp channels and more
- What are relays?
- Relays are electrically operated switches/connectors, which can be used to switch channels on an amplifier and switch other stuff.
- CAUTION: Do NOT connect anything to the relay jacks until you've read the warnings in the manual!
- How many relays does the FX8 have?
- The FX8 has two relays.
- How can I control these relays?
- These are controlled through:
- Scenes - you can use scenes to switch amp channels through relays. This is configured on the preset's Config page.
- Footswitches - you can assign footswitches to the relays per preset, for manual control. Assign the footswitch and configure it on the Footswitch page.
- IMPORTANT: a Relay block in the preset will disable the scene's Relay settings.
- Do the relays support X/Y switching?
- The relays support X/Y switching.
- What are the possible settings?
Off
: nothing is connected.Tip
: the tip is connected to the sleeve.Ring
: the ring is connected to the sleeve.Both
: the tip AND ring are connected to the to sleeve.
- What are the switch modes of the relays?
Latching
: the selected RELAY ON state remains connected and the switch LED remains ON as long as the switch is engaged. Nothing is connected when the switch is OFF.Auto-Off
: the selected RELAY ON state remains connected only for a moment when you press the footswitch. The relay then automatically turns OFF, as does the LED.
- Which cables can be used?
- Depending on the amp, you can use TS or TRS cables.
FRACTAL AUDIO QUOTES
[166] The FX8 will short tip-to-sleeve, ring-to-sleeve, or both. The circuit is designed to handle 200mA of current. If the current generated by that voltage drop is 200mA or less, then the FX8 will not have a problem.
The relays of the FX8 are designed for use ONLY with amplifiers that use “short-to-sleeve” type switching. Do NOT connect the FX8 relays to the switch jacks of an amp that uses voltage differential switching or any other type of switching aside from short-to-sleeve, or serious damage can occur to both units. If you are not 100% sure, contact your amp manufacturer to determine whether your amp is compatible with short-to-sleeve switching. The FX8 relay jacks are compatible with TRS cables, TS cables, or TRS-to-dual-TS split cables. The relays are also fully isolated from the electrical ground of the FX8.
The FX8 features two TRS (Tip-Ring-Sleeve) relays that can be used to switch the channel or other functions of a connected amplifier or device. If the warning above seems stern, that’s because the last thing we want is for anyone to damage their amp or FX8. In fact, short-to-sleeve relay switched amps are quite common, and your amp may well be perfectly compatible. We need to trust and require you however, to understand how your amp works and make the right choices about connecting it to the FX8 relay jacks. Your amp manufacturer should be able to help if you read them the warning above.
[167] The FX8 relay outputs employ a "Short-to-Sleeve" connection. Each relay output can short Tip-to-Sleeve, Ring-to-Sleeve, and Both. If the pedal connection uses a voltage drop to power an LED, the relay circuit on the FX8 is rated for a maximum of 200mA.