Difference between revisions of "Resonator"
(Rough stub article created) |
m (Four-band resonator moved to Resonator) |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | {{Ultra}} | |
| + | [[Image:Resonator_block.jpg|right|350px]] | ||
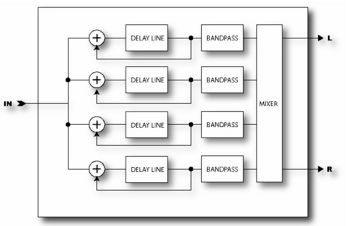
| + | The [[Axe-Fx Ultra]] Resonator is four resonant comb filters in parallel. By tuning the comb filters a metallic or resonant timbre can be achieved from normally non-musical signals. The Resonator works best on transient signals like speech or percussion but can also be used to add unique character to musical inputs. | ||
| − | + | In series with each comb filter is a bandpass filter tuned to the same frequency. The position of these filters can be before or after the comb filters. They are shown in the after position in the diagram above. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | The Resonator can operate in one of two modes: Manual and Chordal. In manual mode control of the filter frequencies is done manually. In chordal mode a base frequency is set and a chord type chosen. The filter frequencies are then set to match the type of chord chosen. | |
| + | |||
| + | ====Parameters==== | ||
| + | *'''MODE''' - Selects between the two modes of operation: manual and chordal. | ||
| + | *'''INGAIN''' - Sets the level into the effect. Since the filters are very resonant overload can occur. This control can be used to reduce the levels. | ||
| + | *'''MASTER FREQ''' - Scales all the frequencies. | ||
| + | *'''MASTER LEVEL''' - Scales all the output levels. | ||
| + | *'''MASTER PAN''' - Scales all the output pans. | ||
| + | *'''MASTER Q''' - Scales all the bandpass filter Q’s. | ||
| + | *'''FREQUENCY n''' - Sets the resonant frequency of the selected filter. | ||
| + | *'''FEEDBACK n''' - Sets the resonance of the selected filter by varying the feedback. | ||
| + | *'''FILTER LOC n''' - Selects the position of the bandpass for the selected filter. | ||
| + | *'''FILTER Q n''' - Sets the Q of the selected bandpass filter. | ||
| + | *'''LEVEL n''' - Sets the output level of the selected filter. | ||
| + | *'''PAN n''' - Sets the panning of the selected filter. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {{stub}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Effect blocks]] | ||
Latest revision as of 17:05, 11 June 2007
The Axe-Fx Ultra Resonator is four resonant comb filters in parallel. By tuning the comb filters a metallic or resonant timbre can be achieved from normally non-musical signals. The Resonator works best on transient signals like speech or percussion but can also be used to add unique character to musical inputs.
In series with each comb filter is a bandpass filter tuned to the same frequency. The position of these filters can be before or after the comb filters. They are shown in the after position in the diagram above.
The Resonator can operate in one of two modes: Manual and Chordal. In manual mode control of the filter frequencies is done manually. In chordal mode a base frequency is set and a chord type chosen. The filter frequencies are then set to match the type of chord chosen.
Parameters
- MODE - Selects between the two modes of operation: manual and chordal.
- INGAIN - Sets the level into the effect. Since the filters are very resonant overload can occur. This control can be used to reduce the levels.
- MASTER FREQ - Scales all the frequencies.
- MASTER LEVEL - Scales all the output levels.
- MASTER PAN - Scales all the output pans.
- MASTER Q - Scales all the bandpass filter Q’s.
- FREQUENCY n - Sets the resonant frequency of the selected filter.
- FEEDBACK n - Sets the resonance of the selected filter by varying the feedback.
- FILTER LOC n - Selects the position of the bandpass for the selected filter.
- FILTER Q n - Sets the Q of the selected bandpass filter.
- LEVEL n - Sets the output level of the selected filter.
- PAN n - Sets the panning of the selected filter.