This is the wiki for products made by Fractal Audio Systems, maintained by members of the community.
November 2025: wiki now covers the AM4 too.
EQ
Contents
PEQ and GEQ: available on which products
- Axe-Fx III: 4x PEQ, 4x GEQ
- FM3: PEQ and GEQ, number of instances not yet known
- Axe-Fx II: 4x PEQ, 4x GEQ
- AX8: 2x PEQ, 2x GEQ
- FX8: 2x PEQ, 2x GEQ
PEQ and GEQ: channels or X/Y switching
- Axe-Fx III: 4 channels
- FM3: 4 channels
- Axe-Fx II XL and XL+: X/Y. There are no MIDI CCs available for X/Y switching on the XL and XL+
- Axe-Fx II Mk I and II: no
- AX8: no
- FX8: no
EQ tools in the processors
The processors provides many EQ tools:
- Parametric EQ block (PEQ)
- Graphic EQ block (GEQ)
- Filter best
- Global EQ for OUT1 and OUT2
- GEQ in the Amp block
- GEQ in the Drive block
- GEQ in the Wah block
- Input EQ in the Amp block (firmware Ares)
- Low Cut and High Cut in several blocks
And more.
All tools are explained in the Owner's Manuals.
Global EQ
There's a 10-band Global EQ on Outputs 1 and 2 on the amp modelers, and on PRE and POST on the FX8. The Global EQ is always active.
The outermost bands are shelving EQ types.
The Global EQs provide a master gain control, which works across all presets. Use this as a quick fix when the output is clipping.
The Global EQ on Output 2 lets you make changes to Output 2, even if Echo Output 2 is set to "Output 1" in I/O.
To reset the Global EQ:
- Axe-Fx III — use the soft knobs
- FM3 — use the soft knobs
- Axe-Fx II — press BYPASS twice fast
- AX8 — press ENTER to reset the selected slider
- FX8 — press ENTER to reset the selected slider. Press ENTER twice quickly to reset all bands and gain.
GEQ
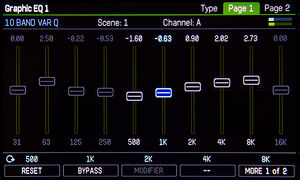
About the GEQ
Types:
- 3 Band Console
- 3 Band Passive
- 4 Band Passive
- 5 Band Constant Q
- 5 Band Passive
- 5 Band Variable Q
- 7 Band Constant Q
- 7 Band Variable Q
- 8 Band Constant Q
- 8 Band Variable Q
- Band 2/3 Octave Constant Q
- Band 2/3 Octave Variable Q
- 10 Band Constant Q
- 10 Band Variable Q
More information about the types:
- The outermost bands in all graphic EQs are shelving types.
- The 3 Band, 4 Band and 5 Band types in the Amp block and GEQ are passive EQs. These simulate the effect of analog EQs such as Pultec.
- The 5 Band type emulates the response of the on-board EQ in the Mesa Boogie Mark series amplifiers. For example, use these settings: Band 80: 7, Band 240: -0.47. Band 750: -7.46. Band 2200: 2.36. Band 6600: 0.
- The 7 Band and 8 Band types emulate popular graphic EQ pedals.
- The 10 Band, 2/3 octave types center the filter frequencies on a narrower range best suited to finely sculpting guitar tones.
- Many “classic” graphic equalizers use variable-Q designs which may be more familiar to some users as opposed to constant-Q filters.
- The various “Passive EQ” types are modeled after classic analog EQs and specifically tuned for guitar amp equalization.
The “Master Q” parameter adjusts the Q of all bands. A value of 1.0 sets the Q to the default value (typically one octave). Lower values increase the bandwidth and overlap of each band, higher values decrease the bandwidth.
"I call the Passive EQs "instant hit record tone". Something about the tone sounds like every hit record from the 70's and 80's to me." source
4-Band (Passive) (fairly low Q)
- Low - (low-shelf 2?) around 50-75 Hz?
- Low/Mid - around 650 Hz
- High/Mid - (high-shelf 2?) around 2500 Hz?
- High - (high-shelf 2?) around 5500 Hz?
5-Band (Passive) (fairly low Q):
- Low - (low-shelf 2?) around 50-75 Hz?
- Low/Mid - around 300 Hz
- Mid - around 800 Hz
- High/Mid - around 1950 Hz?
- High - (high-shelf 2?) around 5500 Hz?
Parameters
| GEQ Parameter | Axe-Fx III | Axe-Fx II | AX8, FX8 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type | yes | ||
| Master Q | yes |
PEQ
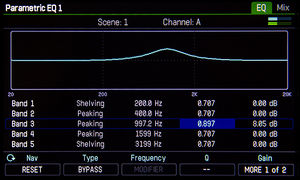
About the PEQ
Types:
- Shelving
- Peaking
- Blocking
- Shelving 2
- Peaking 2
“Shelving 2”: this type recreates the analog shelving filters found on classic mixing consoles. These filters are somewhat quirky and exhibit “overshoot” which gives them a certain musical quality. Set the Q between 0.5 and 0.707 to recreate those classic sounds or experiment with the Q for different amounts of overshoot. These filter types are great for getting that massive sound associated with passive equalization.
Setting the outer bands to "Blocking" is an effective way to cut annoying low and high frequencies with a steep curve.
Parameters
| PEQ Parameter | Axe-Fx III | Axe-Fx II | AX8, FX8 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type | yes | ||
| Frequency | yes | ||
| Q | yes | ||
| Gain | yes |
Tips and tricks
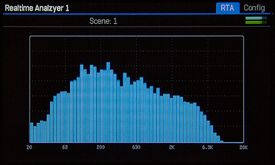
Realtime Analyzer
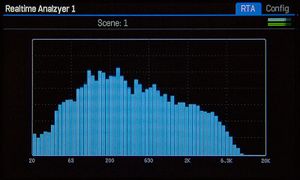
Use the Realtime Analyzer block to see the results of EQ-ing.
PEQ or GEQ as a Global Block
If you want to adjust PEQ settings across multiple presets in one go, add a PEQ or GEQ to these presets and save it as a Global Block (Axe-Fx only).
Pre-EQ in Amp block
The Amp block in the Axe-Fx III has pre-EQ controls and provides several EQ types.
"This was a common technique in the 80's when tracking. If you have an Axe-Fx or other modeler with EQ options you can try it yourself. Put an EQ or Filter block before the amp. A parametric is best. Set the type to Peaking, Frequency to 1 kHz and Q to around 1 and gain to around 6 dB to start. Experiment with the parameters." source
Klon-like boost
Use a PEQ to get a Klon-like boost:
- Level: 6 dB
- Band 1: Shelving2, Q 0.707, 150 Hz, Gain -12
- Band 5: Shelving2, Q 0.707, 2253 Hz, Gain -12
More information
Introduction to EQ-ing guitar sounds
The text below has been written by forum member Clarky.
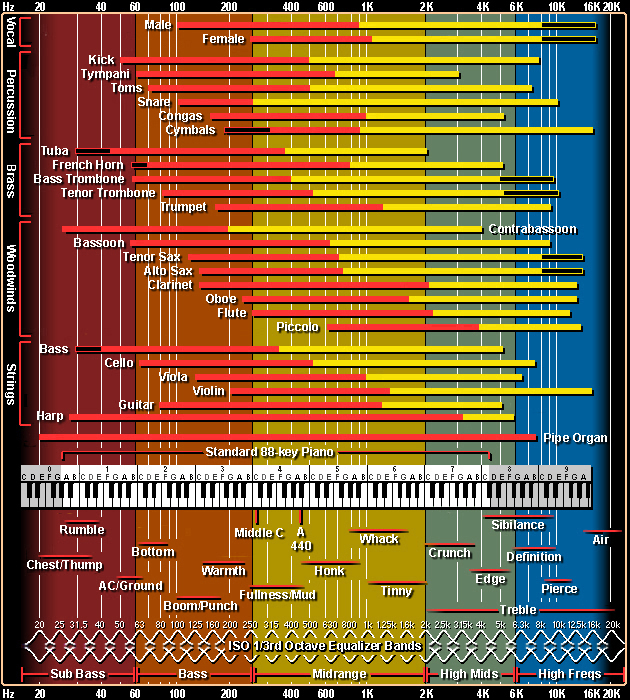
- Graphic EQ – this has multiple frequency bands where the central frequency of each is fixed. Example: If your guitar amp has 4 tone controls - bass, mid, treble, presence - you can think of this as being a 4 band GEQ. Each 'band' [tone control] effects a pretty wide range of frequencies. The 'width' [the frequencies it effects from lowest to highest] of the band is called the Q. In a GEQ you can't change this, you can simply adjust the level of each band by boosting or cutting - using +ve or -ve gain values respectively. An 8 band GEQ is more of the same but by having more bands you have more detailed control and each band's Q is therefore narrower. Try thinking of an 8 band GEQ as having something like - low bass, mid bass, high bass, low mid, mid, high mid, treble, presence. Likewise a 16 band GEQ would have even more controls with narrower Q values that sit in between the bands described above. This being the case a GEQ is pretty straight forward to use. You simply boost / cut the various frequency bands to taste.
- Parametric EQ – far more flexible but there are a few things you need to understand to get the best out of it. Each band has a Q control. This means that you can change the width of the band - and therefore the spread of frequencies that a given band effects. Low Q values create a wide EQ range and high values create very narrow range. This means that you can have very general EQ control with values from 1.0 or lower [not unlike a bass control on an amp], or have precise control [usually corrective] with narrow values such as 1.8 and above. The 'frequency' control in a PEQ allows you to change 'where' in the frequency spectrum the PEQ band is centred [and therefore the frequencies that it acts upon]. So unlike a GEQ with it's fixed bands, a PEQ band can effectively be moved up and down the frequency spectrum and made wide or narrow. In addition, the first and last PEQ bands can also have their filter type altered. Whereas the inner bands use a 'bell shaped curve' to effect the frequency band, the outer bands can be set to bell curves, hi-pass filters [let hi freq pass], low-pass filter [let low freqs pass] and more. This allows yet more EQ refinement.
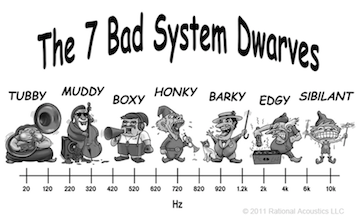
Frequencies important for guitar:
Note: a guitar is actually a tenor instrument [despite all our music being written with a treble clef] so in general terms we can get pretty low [concert tuned]. Our low E is just a little higher than the low C of a cello [which is a bass instrument]. The numbers below are just a rough guide.
- Sub bass – this is below 80Hz - guitars actually produce sounds lower than their lowest notes via sub-harmonics etc. This area of the frequency specrum generates a sense of power and energy in a mix. It's the 'shock and awe' area of the mix. However too much can cause a loss of clarity. Many produces will cut everything below 50Hz to tighten the tone.
- Bass – 100Hz to 400Hz - this is where all the power is in guitar terms. Too much will destroy your definition and make you sound woolly.
- Low mids – 400Hz to 800Hz - this is where your thump is. Low mids and bass beth generate a lot of energy [electrically and in terms of moving air] and at times can get in each other's way. If you want deep bass then scoop these out a little. But beware, a lack of low-mids will get you lost in the mix. The relationship between bass and low mids is critical. Tip - Never lose sight of the fact that your bassist provides most of the the deep bass. So often you can get away with using less bass and more low-mid in the mix. and between the two of you there will be plenty of low stuff in the mix. It's not unusual for tones that sound killer in isolation to not sit well in a mix, and in contrast, tones that sound a little lacking in the low stuff to sound great in the mix. It's all about the different instruments leaving space for each other and inter-acting with each other.
- Mids – centred around 1KHz - this is what cuts you through the mix. Too much and you'll sound nasal, not enough and you'll vanish in the mix.
- High mids – centred around 2.5KHz to 3KHz - this is where you get your definition. Too much and you sound shrill, not enough and the leading edges of your notes will vanish. And it's for this reason that legato centric players [in the Satriani mould] tend to like to roll off this band a little to 'warm up' and 'soften' the tone. Whereas full-on riffers, alt-picking shredders and percussive players [like funk] like this band to be a little stronger to add attack and definition.
- Treble – centred around the 5KHz area - this adds all the sparkling highs. Too much becomes piercing and brittle sounding. Too little make your tone sound confined and lifeless. For those of you that create presets in stereo, it's the upper frequency ranges [high-mids, treble and presence] that convey the sense of 'spread'. The general rule is that the higher the frequency, the narrower the beam [from the speaker cone] is and therefore the more directional it becomes.
- Presence ['air'] – is from 7KHz or 8KHz and up - guitars don't do a great deal up there. Some effects though will generate harmonics up there [especially distortion centric effects]. In the studio you'd tend to use this on the mix overall or on cymbals / synths etc. Depending on the fx you have running in the chain it is worth experimenting with this band to see if it adds or fixes something, but don't be too surprised if you do not perceive a great deal happening. I tend to think that the general tonal impact is not be as strong as with the treble bands.